Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...
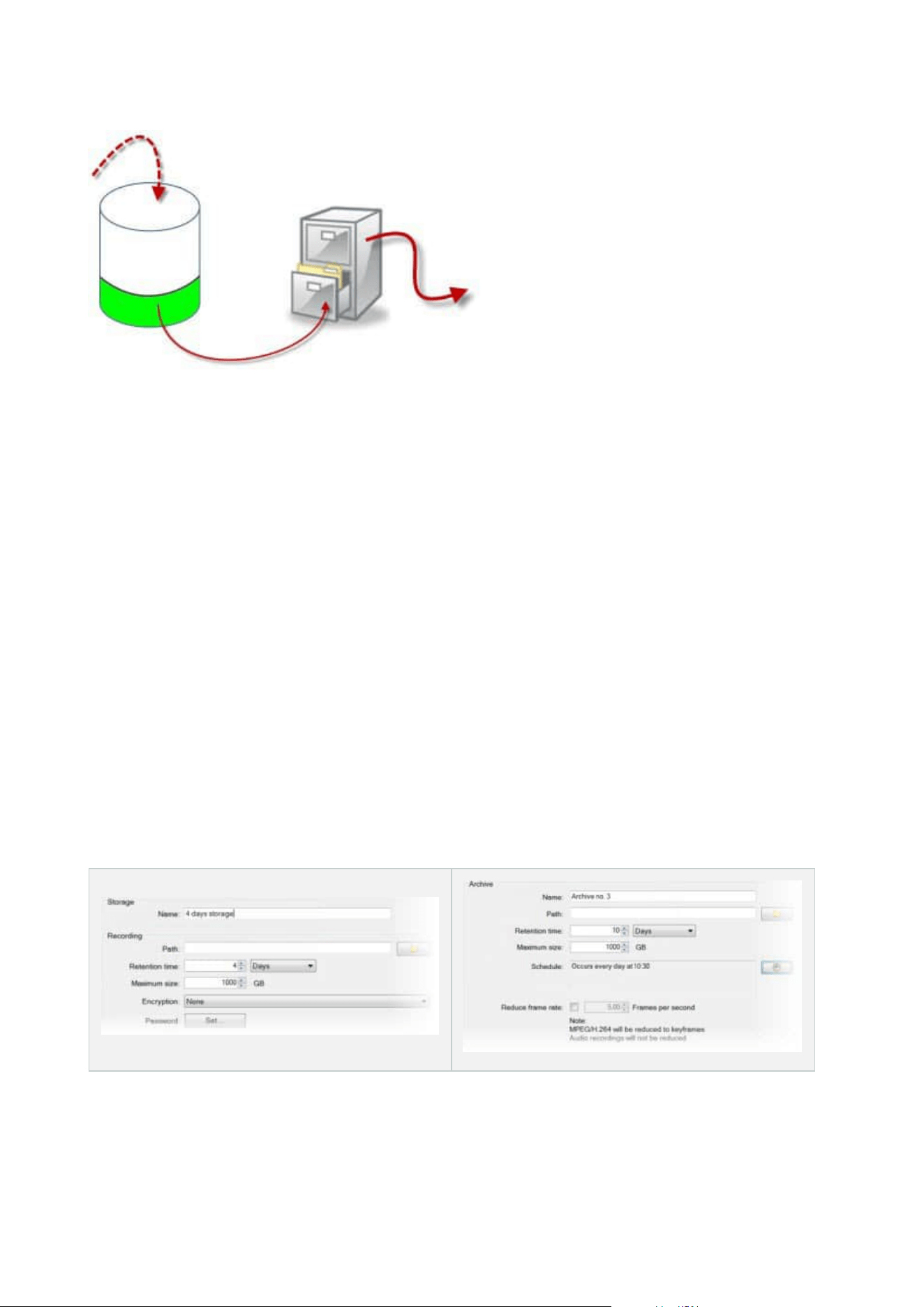
By means of retention time and size setting for the recording storage, exemplified by the white area in the
cylinder, you define how old recordings must be before they are archived. In our illustrated example, you
archive the recordings when they are old enough to be archived.
The retention time and size setting for archives define how long the recordings remain in the archive.
Recordings remain in the archive for the time specified, or until the archive has reached the specified size limit.
When these settings are met, the system begins to overwrite old recordings in the archive.
The archiving schedule defines how often and at what times archiving takes place.
FPS determines the size of the data in the databases.
To archive your recordings, you must set all these parameters up in accordance with each other. This means
that the retention period of the next archive must always be longer than the retention period of a current
archive or recording database. This is because the number of retention days stated for an archive includes all
retention stated earlier in the process. Archiving must also always take place more frequently than the
retention period, otherwise you risk losing data. If you have a retention time of 24 hours, any data older than
24 hours is deleted. Therefore, to get your data safely moved to the next archive, it is important to run
archiving more often than every 24 hours.
Example: These storages (image to the left) have a retention time of 4 days and the following archive (image to
the right) a retention time of 10 days. Archiving is set to occur every day at 10:30, ensuring a much more
frequent archiving than retention time.
Administrator manual | XProtect® VMS 2023 R1
58 | Overview
Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...
