Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...
SLIM DUCT TECHNICAL OVERVIEW
F-7
ENGLISH
Topic Title
Testing
Testing Temperature Sensors
The easiest problems to solve will involve codes that are
related to potential failure of temperature sensors. Common
problems may include loose connections, open electrically,
and out of calibration. Checking the condition of the sensors
requires a temperature probe and an ohmmeter.
The Reference Section of this manual contains temperature
resistance tables that can be used to check the calibration
of the sensors. The measured resistance must be within the
tolerances printed on the top of the tables.
1. Conrm the sensor is rmly attached to the circuit board
connection plug.
2. Remove the sensor wires from the connection plug by
releasing holding tension on the plugs tension tab.
3. Use an ohmmeter to test the electrical resistance of the
sensor.
4. Measure the air temperature near the sensor and compare
the required resistance against measured resistance.
(refer to charts in reference section) If the sensor is
within calibration, the sensor is good. If the sensor is out
of calibration, replace the sensor. (Tube Sensors should
be removed from socket and exposed to air temperature
during test.)
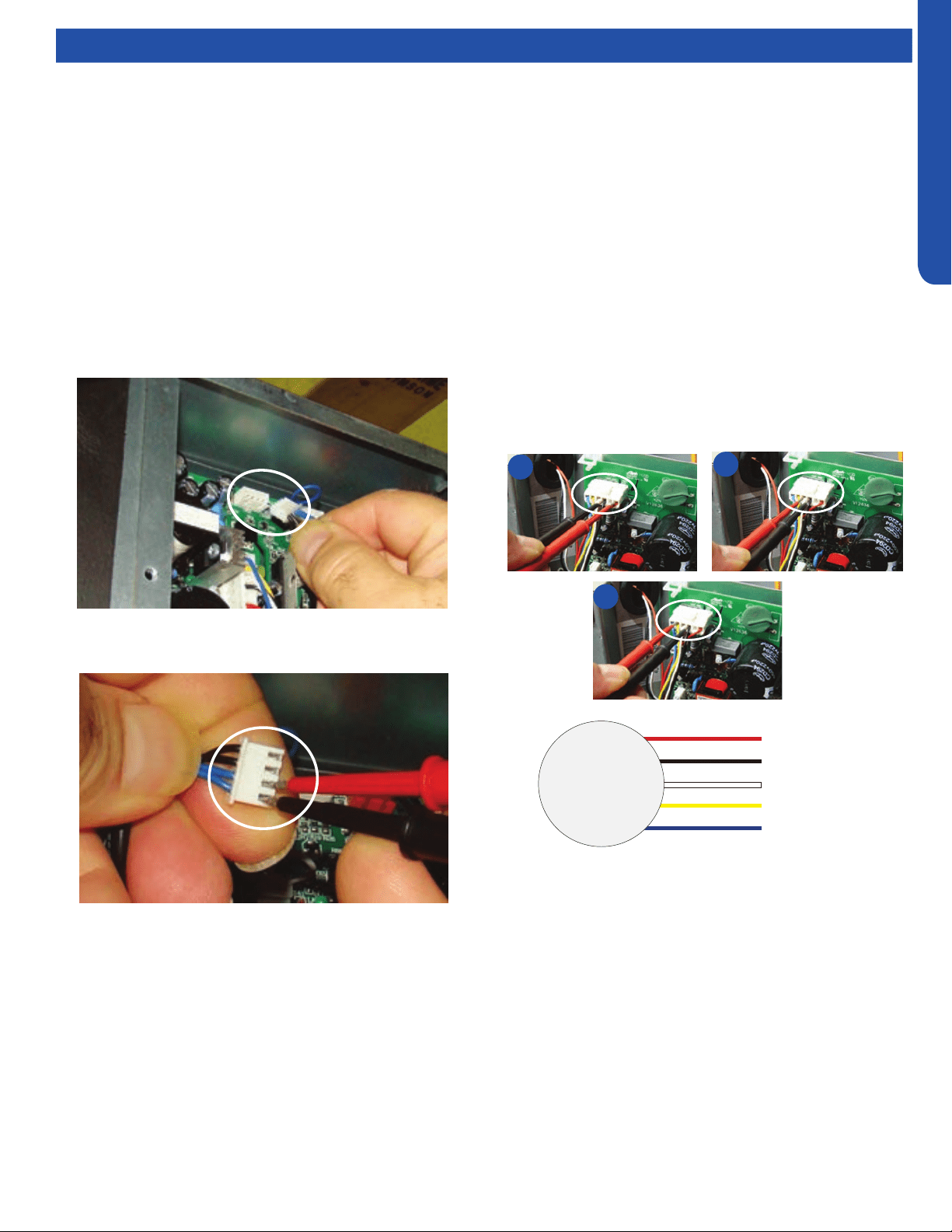
If The Indoor Fan Motor Does Not Run:
1. Remove the front cover and access the fan motor circuit
board connection.
2. Reset power and turn the remote control fan command to
Fan On mode.
Motor Test:
1. If the motor doesn’t run, check for 310VDC between Pins 1
and 3. If it is not present, the indoor board is bad. If voltage
is present, continue on.
2. Check the voltage between Pins 3 and 4. The voltage
should be +15VDC. If it is not present, the board is bad. If
voltage is present, continue on.
3. Check for voltage between Pins 3 and 6. If no DC voltage is
present, the board is bad. If voltage is present, change the
motor.
Indoor Fan Motor Voltage Check
1
2
3
DC Motor
+310 VDC
DC Ground
+15 VDC
Signal
Feedback
Red
Black
White
Yellow
Blue
Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...