Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...
16
DN606 Automotive Diagnostic Tool User's Manual
Pending Code. The computer does not command the MIL on at this time. If the
fault is sensed again on the second trip, the computer commands the MIL “On,”
and saves the code in its long-term memory.
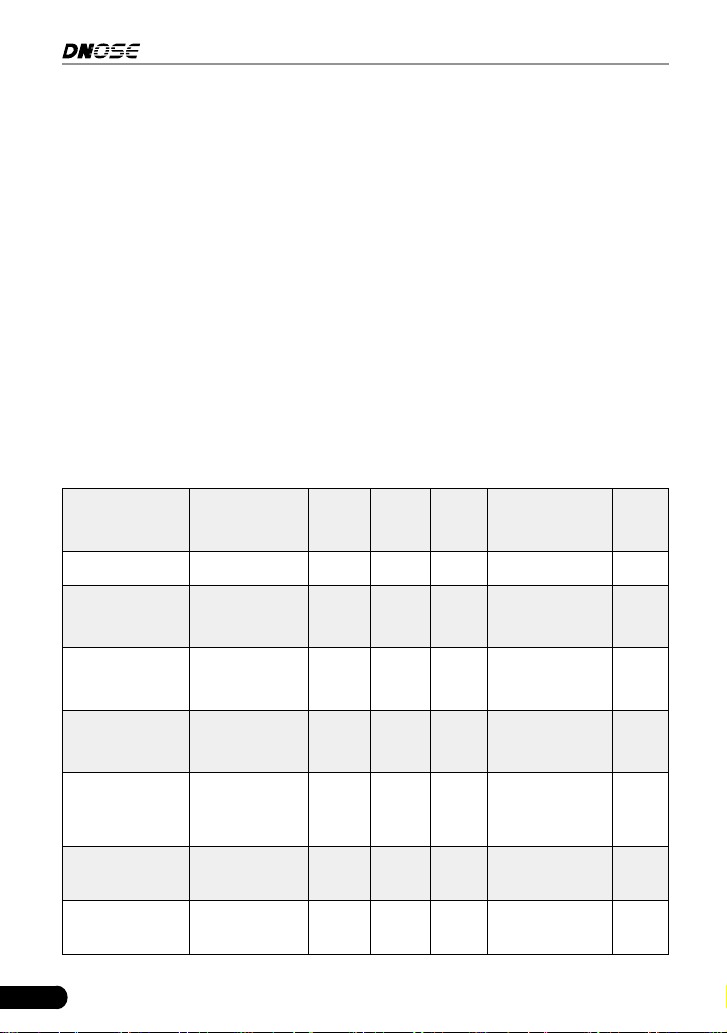
2.6.3 OBD II Reference Table
The table below lists current OBD II Monitors, and indicates the following for
each Monitor:
A. Monitor Type (how often does the Monitor run; Continuous or Once per trip).
B. Number of trips needed, with a fault present, to set a pending DTC.
C. Number of consecutive trips needed, with a fault present, to command the
MIL “On” and store a DTC.
D. Number of trips needed, with no faults present, to erase a Pending DTC.
E. Number and type of trips or drive cycles needed, with no faults present, to
turn off the MIL.
F. Number of warm-up periods needed to erase the DTC from the computer’s
memory after the MIL is turned off.
Name of
Monitor
A B C D E F
CCM Continuous 1 2 1 3 40
Misre Monitor
(Type 1 and 3)
Continuous 1 2 1
3 - similar
conditions
80
Misre Monitor
(Type 2)
Continuous 1 1 1
3 - similar
conditions
80
Fuel System
Monitor
Continuous 1 1 or 2 1
3 - similar
conditions
80
Catalytic
Converter
Monitor
Once per trip 1 2 1 3 trips 40
O
2
Sensor
Monitor
Once per trip 1 2 1 3 trips 40
O
2
Sensor
Heater Monitor
Once per trip 1 2 1 3 trips 40
Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...