Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...
11
A SECOND
LATER....
CODE NUMBER
The second number shown after the
code sequence number is the code
itself (31-99, example" "31"). Refer to
the chart on the following page for an
explanation of each code.
CODE SEQUENCE NUMBER
The first number shown is the most
recent code (example: "01"). The
display will show the sequence of
codes that occurred starting with
"01" and going up to code "20".
e. Using the display, observed the advanced diagnostic codes>
f.
g. The digits used in advanced diagnostic codes are hexadecimal values. 0-9 and A-F. Note the distinction between a B and a 6.
Advanced
number
displayed
Value Blank
(no code)
01 23 45 67 89 Ab Cd EF
h. Record all of the advanced error codes. There can be up to 20 entries.
11. Advanced diagnostic codes that pertain to the LMWEKITU.
Code Description Code Description
AB – Loss of Bluetooth wireless communication for an open edge. Check
the transmission of those transmitter connected and set up for edges in
the open direction. Go to step 12).
AD – Loss of I2C communication for an open edge. If there is an edge in both directions,
AD and AE may both be showing in the advanced diagnostic log. Go to step 13).
AC – Loss of Bluetooth wireless communication for a close edge. Check
the transmission of those transmitter connected and set up for edges in
the close direction. Go to step 12).
AE – Loss of I2C communication for a close edge. If there is an edge in both directions,
AD and AE may both be showing in the advanced diagnostic log. Go to step 13).
a. NOTE: Not all advanced diagnostic indicate that there is a problem with the logic board or operator. Most diagnostic codes are factory settings and don’t represent problems or issues.
12. Troubleshooting Bluetooth wireless edge communications (AB and AC).
a. Factors that can compromise the Bluetooth wireless communications.
i. Electromagnetic Interference: There could be nearby electronics that could be intentionally or non-intentionally broadcasting at the frequencies that the Bluetooth transmitters could be
broadcasting on:
1. LED and florescent lighting systems.
a. See if the frequency of the diagnostic codes decrease when the lighting systems are turned off.
2. Wi-Fi
®
, security systems, radio, cellular, and other wireless equipment.
a. Try to disable if it is all possible.
b. Shorten the distance between transmitter and receiver.
3. Motor magnetic fields, possibly including a motor installed in the operator.
a. Ensure that the receiver is installed in the recommended location.
b. Try moving the receiver to different locations and different orientations.
4. NOTE: If a wireless Bluetooth headset being used by a technician has interference problems with his signal, the same is probably happening with the transmitter to receiver on the LMWEKITU.
ii. Week batteries in the transmitter.
1. Change the batteries, ensuring that a Lithium ion battery is used.
iii. Distance between transmitter and receiver.
1. Try shortening the distance between the transmitter and receiver.
iv. Loose connections at the wire between the edge and transmitter causing intermittent drop outs.
1. Open the edge cap and transmitter.
2. Check for continuity using an Ohmmeter.
3. Inspect the monitor resistor’s leads for corrosion.
v. Water in the edge, transmitter or receiver.
1. Open the edge, transmitter and receiver to make sure that no moisture is present.
2. Inspect the monitor resistor’s leads for corrosion. This resistor is usually at the bottom of the edge where moisture can accumulate.
vi. Bad transmitter or receiver.
1. Try other alternatives first prior to suspecting transmitter or receiver.
vii. All (or some) of the above. Try multiple solutions.
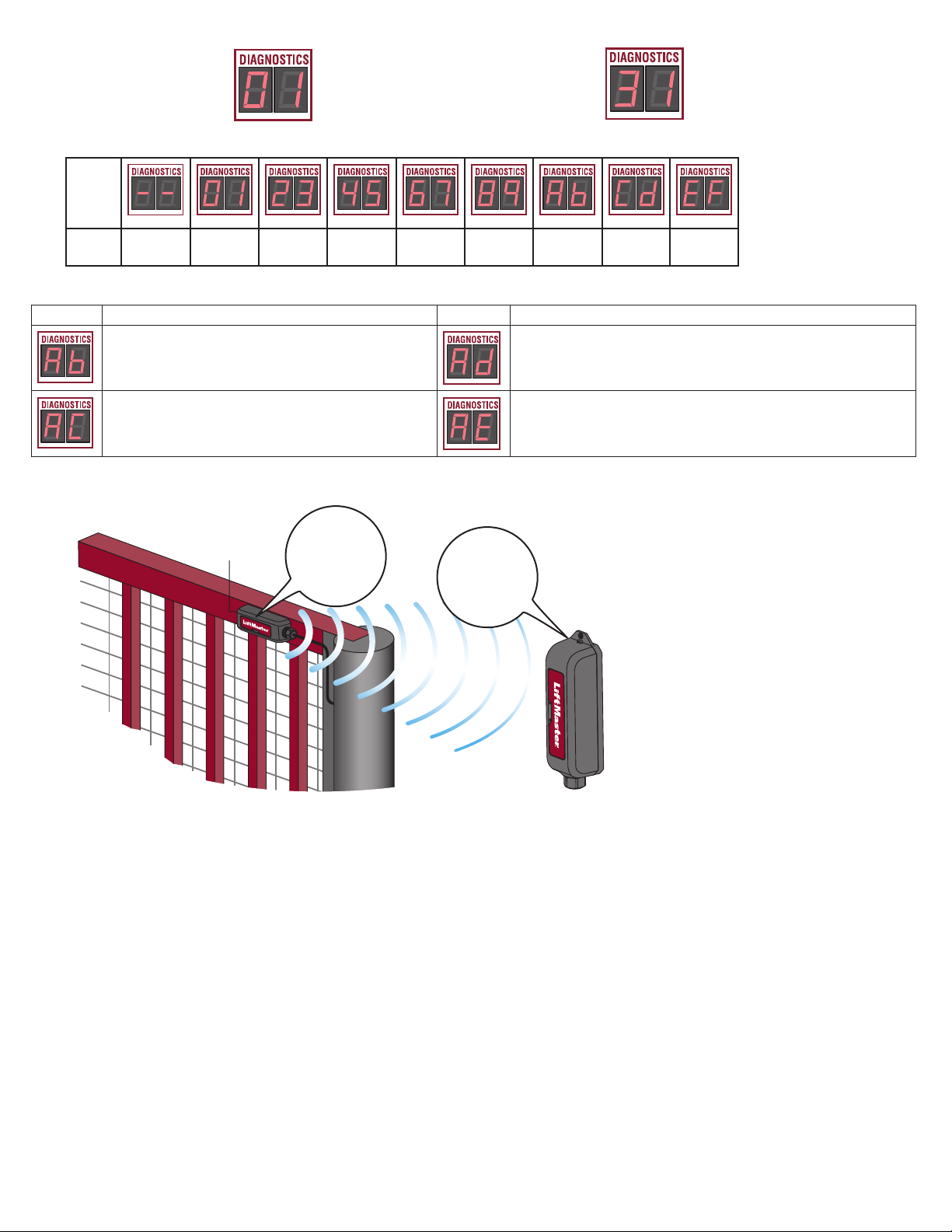
Blue tooth
RF energy
Transmitter
Advanced code
AB from open
edge. Advanced
code AC from
close edge.
Advanced code
AB from open
edge. Advanced
code AC from
close edge.
Receiver
Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...