Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...
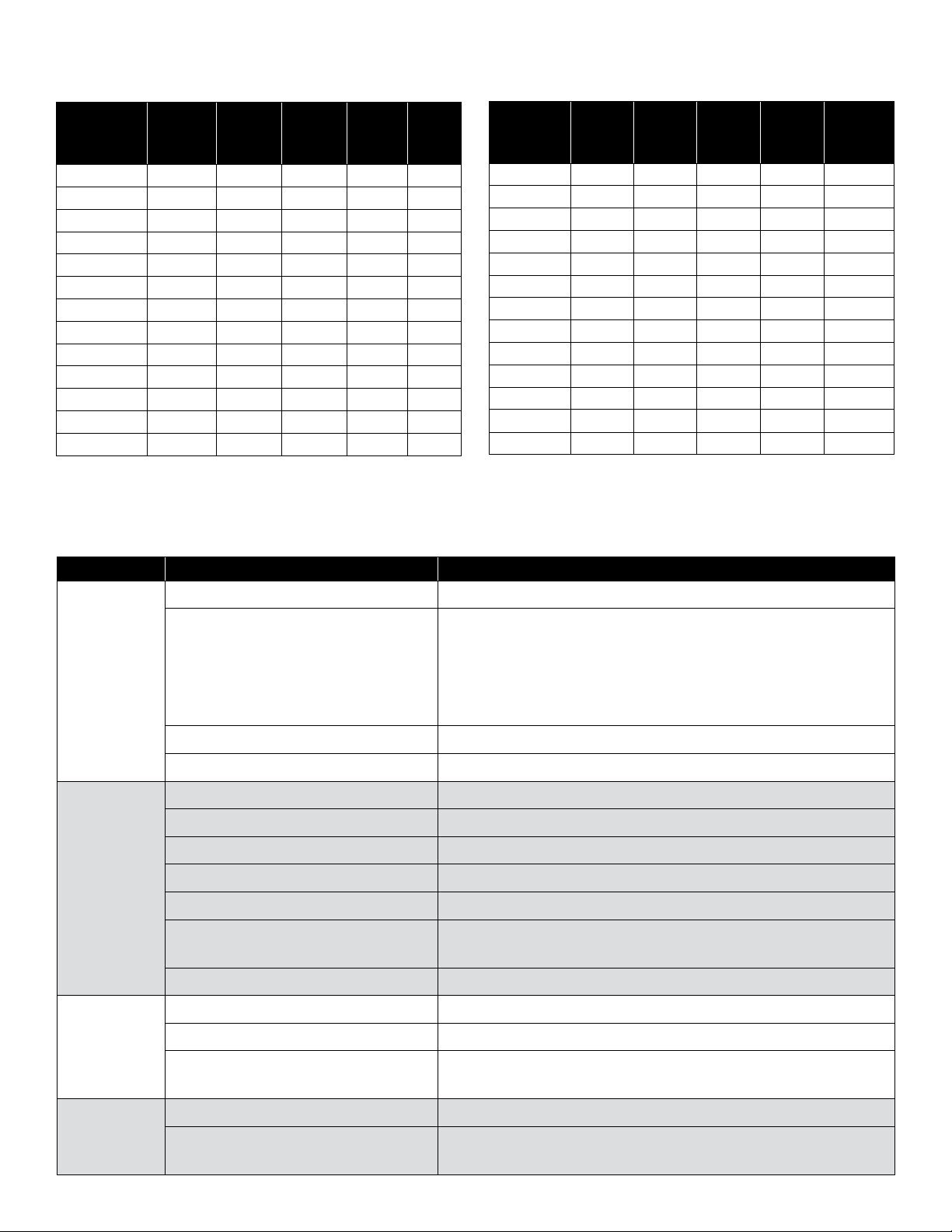
Problem Possible Cause Remedy
Failure to pump
Pump not properly primed. Make sure pump casing and suction line are full of water. See priming instructions.
Speed too low.
s WARNING
!
ELECTRICAL PRECAUTIONS. All wiring, electrical
connections and system grounding must comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC)
and with any local codes and ordinances. Employ a licensed electrician. Check voltage at
motor terminals and at meter when pump is operating. If low, refer to wiring instructions
or check with your power company. Check loose connections.
Total head more than for which pump was intended. A pump designed for higher head needed.
Suction lift is too great. Locate pump closer to source of water. Make sure suction piping is large enough.
Reduced capacity
and/or head
Air pockets or leaks in suction line. Check suction piping.
Clogged impeller. Remove and clean.
Strainer too small or clogged. Use larger strainer or clean.
Insucient submergence of suction line. Add lengths of suction pipe to keep submerged end well below the water surface.
Excessive suction lift. If caused by suction pipe friction, enlarge piping.
Total head more than that for which
the pump was intended.
A pump designed for higher head is needed.
Excessively worn impeller. Order replacement parts using Replacement Parts list.
Pump loses prime
Air leaks in suction line. Check suction piping.
Excessive lift and operating too near shut-o point. Move pump nearer water level.
Water level drops while pumping,
uncovering suction piping.
Check water supply. Add length of pipe to suction to keep submerged end under water.
Mechanical
troubles and noise
Bent shaft and/or damaged bearings. Take motor to authorized motor repair shop.
Suction and/or discharge piping not properly
supported and anchored.
See that all piping is supported to relieve strain on pump assembly.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Nominal
Pipe Size
U.S. GPM 3/4" 1" 1-1/4'' 1-1/2'' 2''
4 3.75 1.15 0.30 0.14 –
5 5.66 1.75 0.46 0.22 –
6 7.95 2.45 0.65 0.31 –
7 10.60 3.25 0.86 0.41 –
8 13.50 4.16 1.10 0.52 –
9 16.80 5.17 1.35 0.65 –
10 20.40 6.31 1.67 0.79 0.23
11 24.40 7.58 1.98 0.95 0.27
12 28.60 8.85 2.33 1.10 0.32
14 38.00 11.80 3.10 1.46 0.43
16 48.60 15.10 3.96 1.87 0.55
18 60.50 18.70 4.93 2.33 0.69
20 73.50 22.80 6.00 2.83 0.84
Loss of head in feet due to friction per 100 feet of pipe
Table 2 - FRICTION LOSS FOR PLASTIC PIPE*
Nominal
Pipe Size
L/Min. 20 mm 25 mm 32 mm 40 mm 50 mm
15 3.7 1.15 0.30 0.13 –
20 5.3 1.64 0.43 0.19 –
25 7.1 2.18 0.56 0.27 –
30 13.5 4.13 1.08 0.49 –
35 16.3 5.00 1.31 0.61 –
40 23.5 7.30 1.90 0.88 0.25
45 28.3 8.74 2.31 1.07 0.29
50 34.2 10.60 2.79 1.32 0.38
55 40.7 12.60 3.32 1.56 0.46
60 48.1 14.90 3.92 1.85 0.54
65 55.7 17.30 4.45 2.15 0.63
70 63.8 19.70 5.20 2.46 0.73
75 72.2 22.40 5.89 2.78 0.83
Loss of head in meters due to friction per 100 meters of pipe
*For galvanized pipe, double the figures.
8
Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...