Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...
26 Alphabetical Listing
cos()
µ key
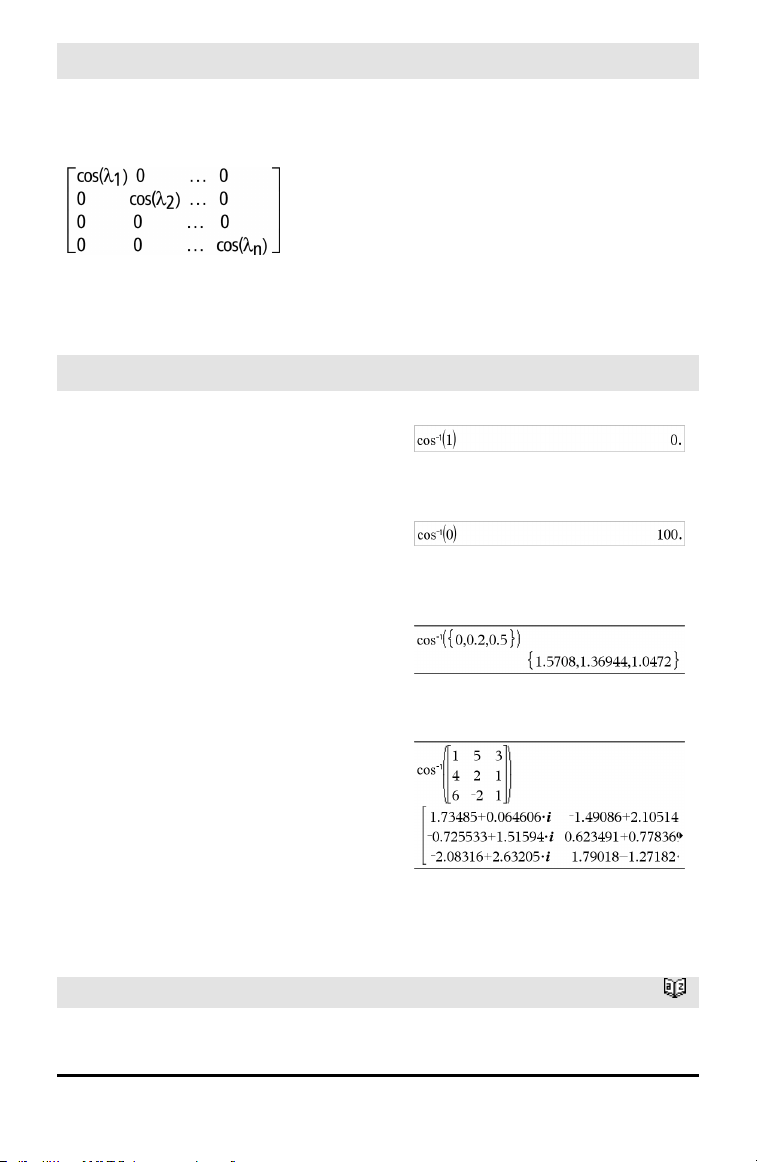
Then A = X B X⁻¹ and f(A) = X f(B) X⁻¹. For
example, cos(A) = X cos(B) X⁻¹ where:
cos(B) =
All computations are performed using
floating-point arithmetic.
cos⁻¹()
µ key
cos⁻¹(Value1) ⇒ value
cos⁻¹(List1) ⇒ list
cos⁻¹(Value1) returns the angle whose
cosine is Value1.
cos⁻¹(List1) returns a list of the inverse
cosines of each element of List1.
Note: The result is returned as a degree,
gradian or radian angle, according to the
current angle mode setting.
Note: You can insert this function from the
keyboard by typing arccos(...).
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
cos⁻¹(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix inverse cosine of
squareMatrix1. This is not the same as
calculating the inverse cosine of each
element. For information about the
calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The
result always contains floating-point
numbers.
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular
Complex Format:
To see the entire result, press £ and then
use ¡and¢ to move the cursor.
cosh()
Catalog >
In Degree angle mode:
Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...