Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...
Seat belts 21
Safety First Operating instructions Tips and Maintenance Technical Data
Why wear seat belts?
Frontal collisions and the laws of physics
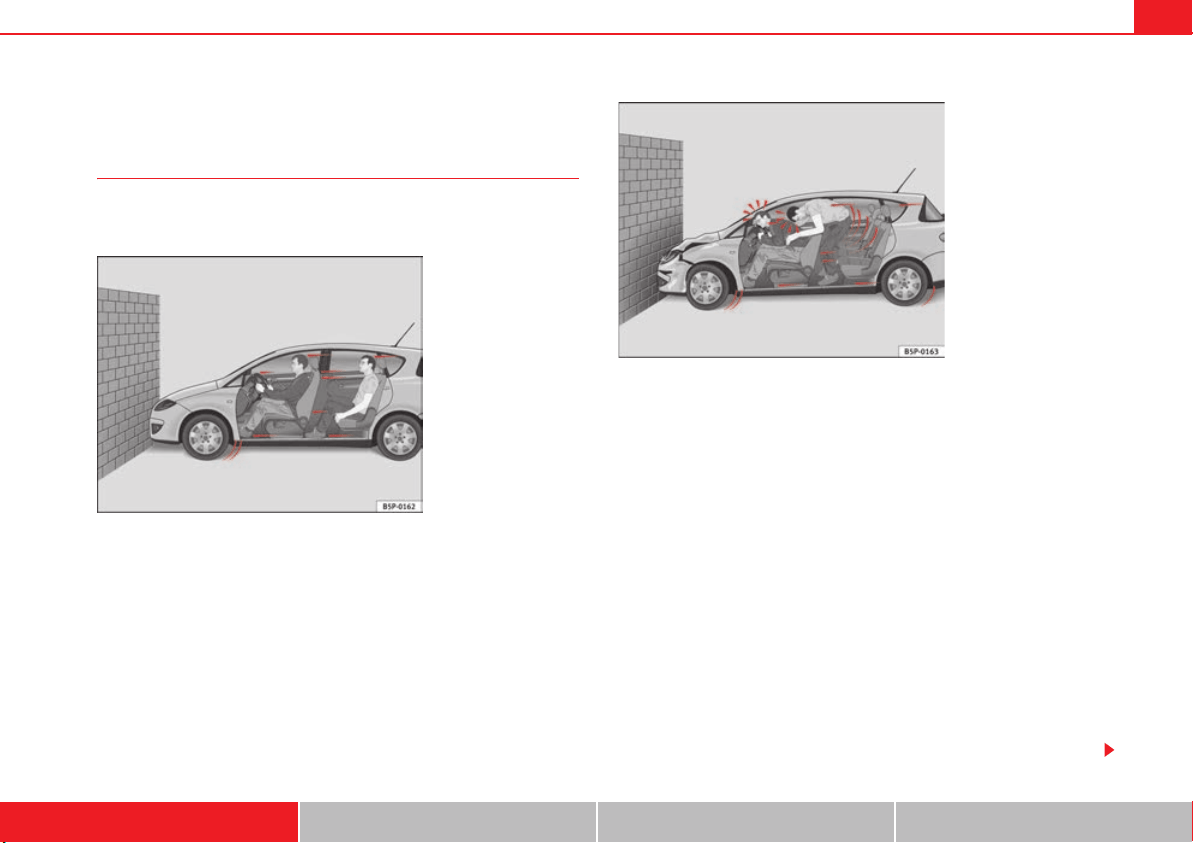
In the event of a frontal collision, a large amount of kinetic
energy is generated.
It is easy to explain how the laws of physics work in the case of a head-on
collision: When a vehicle starts moving ⇒ fig. 7 there is a certain amount of
energy known as “kinetic energy”, both in the vehicle and in the occupants.
The amount of “kinetic energy” depends on the speed of the vehicle and the
weight of the vehicle and passengers. The higher the speed and the greater
the weight, the more energy there is to be “released” in an accident.
The most significant factor, however, is the speed of the vehicle. If the speed
doubles from 25 km/h to 50 km/h, for example, the kinetic energy increases
by a factor of four.
Because the passengers in our example are not restrained by seat belts, the
entire amount of kinetic energy has to be absorbed at the point of impact
⇒ fig. 8.
Even at speeds of 30 km/h to 50 km/h, the forces acting on bodies in a colli-
sion can easily exceed one tonne (1,000 kg). At greater speed these forces
are even higher.
Passengers not wearing seat belts are not “attached” to the vehicle. In a
frontal collision they will continue to move forward at the speed their vehicle
Fig. 7 Vehicle about to hit
wall: the occupants are
not wearing seatbelts
Fig. 8 The vehicle hits
the wall: the occupants
are not wearing seatbelts
toledo ingles.book Seite 21 Mittwoch, 11. April 2007 1:25 13
Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...