Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...
CUTTING AIDS AND ACCESSORIES
CUT OFF GAUGE
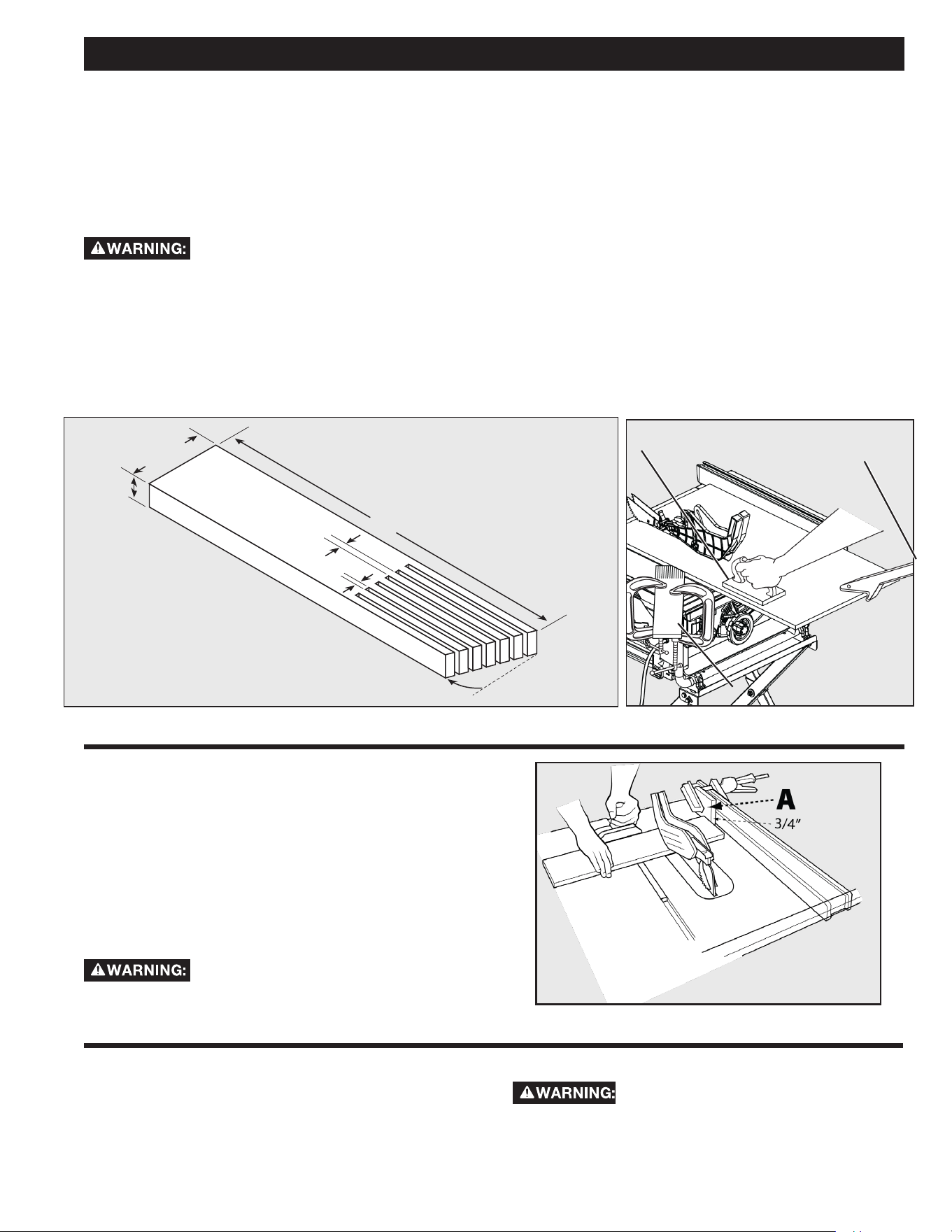
When crosscutting a number of pieces to the same length,
you can clamp a block of wood (A) (See Figure 39) to the
fence and use it as a cut-off gauge. The block (A) must be at
least 3/4-inch (19 mm) thick to prevent the cut off piece from
binding between the blade and the fence. Once the cut-off
length is determined, lock the fence and use the miter gauge
to feed the workpiece into the blade.
Always position the cut-off gauge in front of
the saw blade.
FIGURE 39
FIGURE 38 FIGURE 38A
FEATHERBOARD
1. Select a solid piece of lumber approximately 3/4-inch
thick, 2 1/2-inches wide and 12-inches long.
2. Mark the center width on one end of stock. Miter width
to 70° (see miter cut section for information on miter
cuts).
3. Set rip fence to allow approximately a 1/4-inch “nger”
to be cut in the stock.
4. Feed stock only to mark previously made at 6 inches.
5. Turn saw o and allow blade to completely stop rotating
before removing stock.
6. Reset rip fence and cut spaced rips into workpiece
to allow approximately 1/4-inch ngers and 1/8-inch
spaces between ngers.
Featherboards are used to keep the work in contact with
the fence and table (Figure 38), and help prevent kickback.
Featherboards are especially useful when ripping small
workpieces and for completing non-through cuts. The end is
angled with a series of narrow slots to give a friction hold on
the workpiece, It is locked in place on the table or fence with a
c-clamp.
To avoid binding between the workpiece and
the blade, make sure a horizontal feather board presses only
on the uncut portion of the workpiece in front of the blade.
Dimensions for making a typical featherboard are shown in
Figure 38. Make your featherboard from a straight piece of
wood that is free of knots and cracks. Clamp featherboards to
the fence and/or table so that the featherboard will hold the
workpiece against the fence or table.
FIGURE 38
JIGS
Do not attempt to create or use a jig unless
you are thoroughly familiar with table saw
safety. Do not use any jig that could result in pinching a kerf
or jamming the workpiece between the jig and the blade.
Incorrect setups may cause kickback which could result in
serious injury.
Jigs may be created with a variety of special set-ups to control
particular workpiece shapes for particular cuts. Guidance on
how to make specialized jigs can be found in woodworking and
carpentry websites and publications.
3/4 in.3/4 in.
12 in.12 in.
70˚70˚
2 1/2 in.2 1/2 in.
1/4 in.1/4 in.
1/8 in.1/8 in.
PUSH BLOCK PUSH BLOCK
FEATHER BOARD FEATHER BOARD
PUSH STICK PUSH STICK
29
Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...