Documents: Go to download!
- Owner's manual - (English)
WiFi Wireless Gaming Router User Manual
GETTING STARTED
Router Setup
IMPORTANT!
- Use a wired connection when setting up your wireless router to avoid possible setup problems.
- Before setting up your ASUS wireless router, do the following:
- If you are replacing an existing router, disconnect it from your network.
- Disconnect the cables/wires from your existing modem setup. If your modem has a backup battery, remove it as well.
- Reboot your cable modem and computer (recommended).
A. Wired connection
NOTE: You can use either a straight-through cable or a crossover cable for wired connection.
To set up your wireless router via wired connection:
1. Plug your router into a power outlet and power it on. Connect the network cable from your computer to a LAN port on your router.
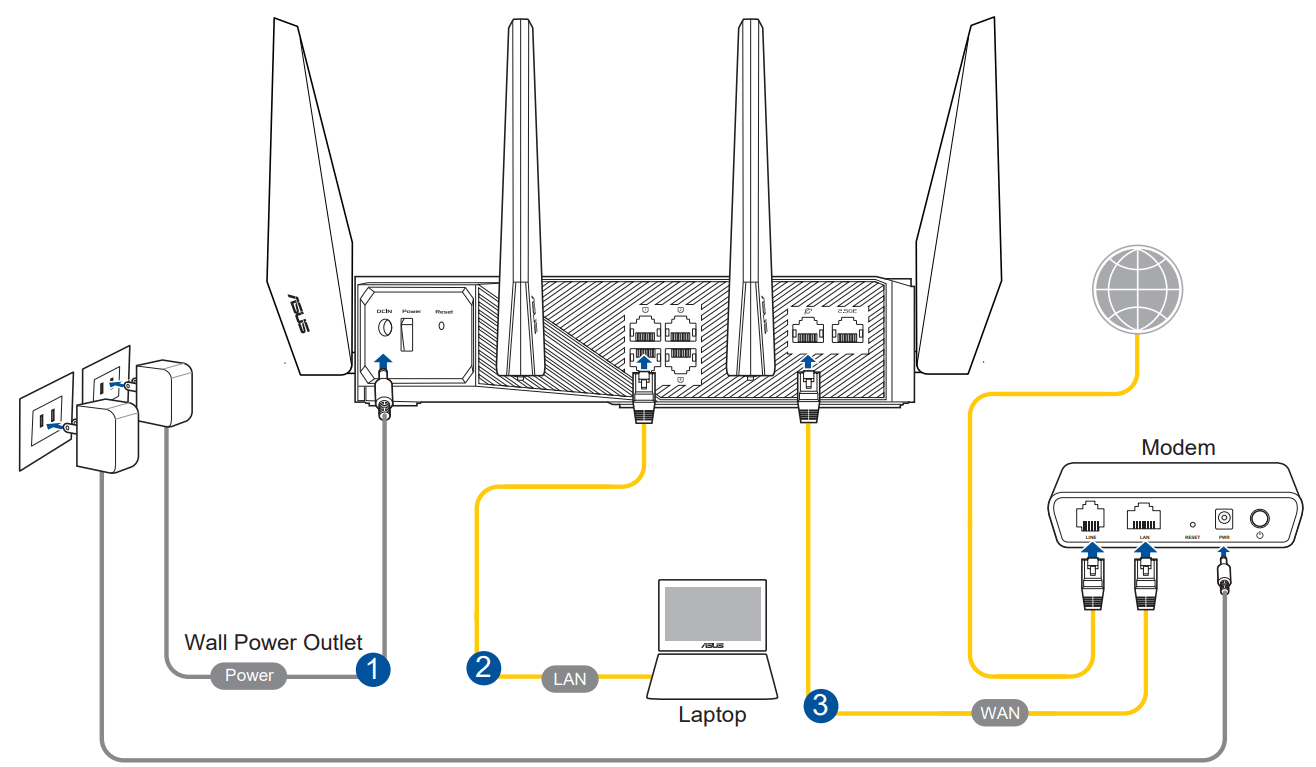
2. The web GUI launches automatically when you open a web browser. If it does not auto-launch, enter http://router.asus.com
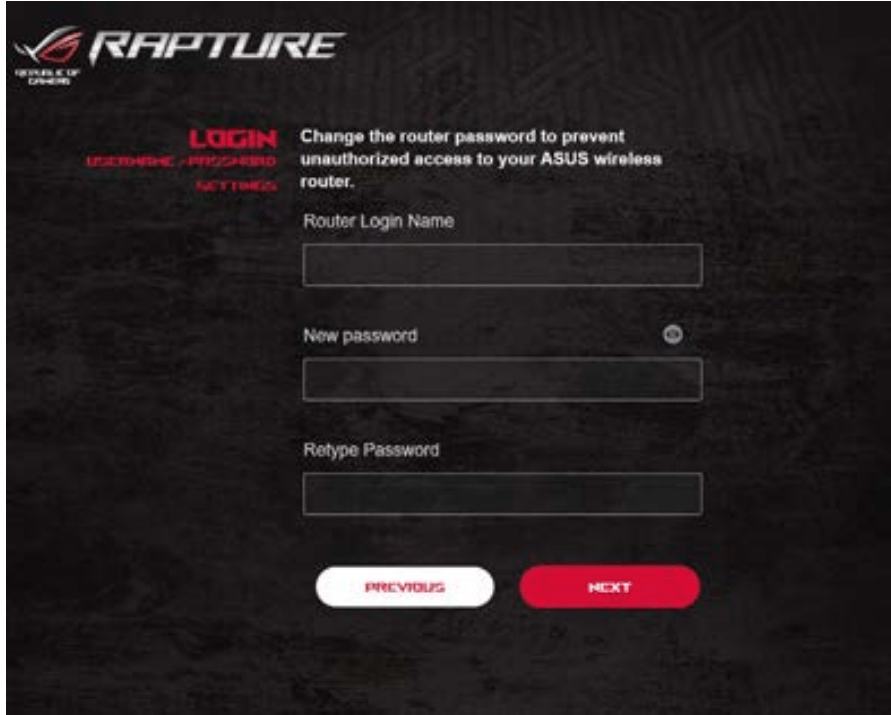
3. Set up a password for your router to prevent unauthorized access.
B. Wireless connection
To set up your wireless router via wireless connection:
1. Plug your router into a power outlet and power it on.
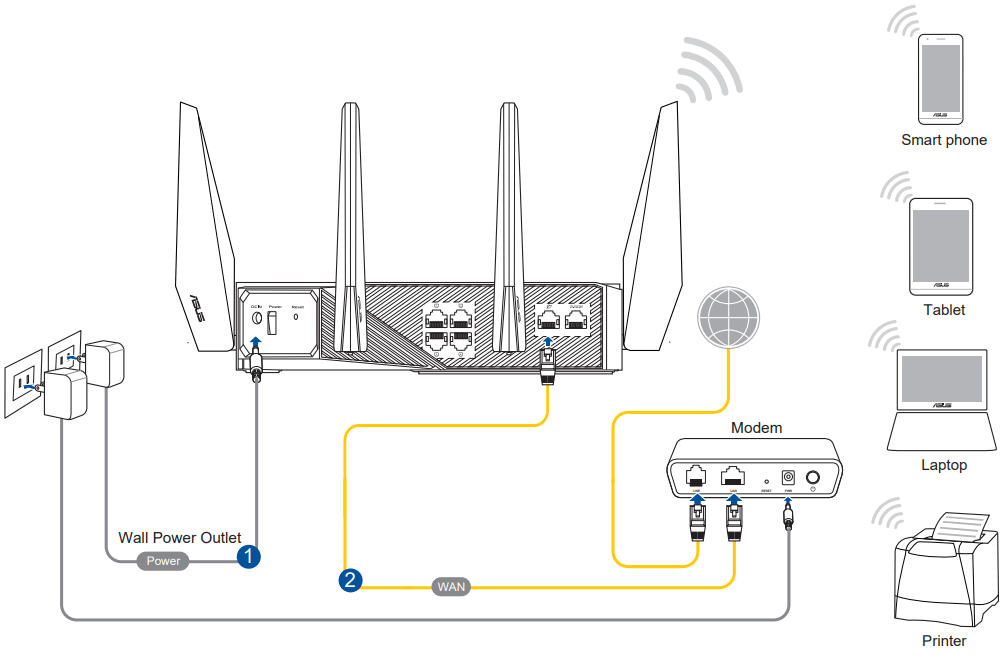
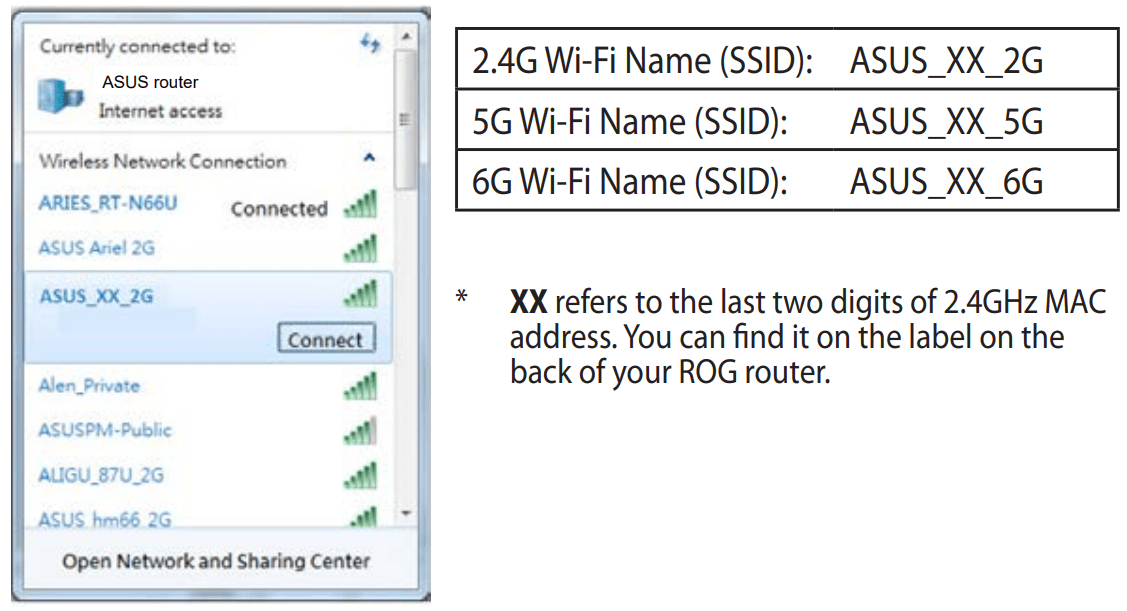
2. Connect to the network name(SSID) shown on the product label on the back side of the router. For better network security, change to a unique SSID and assign a password.
3. Once connected, the web GUI launches automatically when you open a web browser. If it does not auto-launch, enter http://router.asus.com.
4. Set up a password for your router to prevent unauthorized access.
NOTES:
- For details on connecting to a wireless network, refer to the WLAN adapter’s user manual.
- To set up the security settings for your network, refer to the section Setting up the wireless security settings in Chapter 3 of this user manual.
Quick Internet Setup (QIS) with Auto detection
The Quick Internet Setup (QIS) function guides you in quickly setting up your Internet connection.
NOTE: When setting the Internet connection for the first time, press the Reset button on your wireless router to reset it to its factory default settings.
To use QIS with auto-detection:
1. Launch a web browser. You will be redirected to the ASUS Setup Wizard (Quick Internet Setup). If not, key in http://router.asus.com manually.

2. The wireless router automatically detects if your ISP connection type is Dynamic IP, PPPoE, PPTP and L2TP. Key in the necessary information for your ISP connection type.
IMPORTANT! Obtain the necessary information from your ISP about the Internet connection type.
NOTES:
- The auto-detection of your ISP connection type takes place when you configure the wireless router for the first time or when your wireless router is reset to its default settings.
- If QIS failed to detect your Internet connection type, click Skip to manual setting and manually configure your connection settings.

3. Assign the wireless network name (SSID) and security key for your 2.4GHz, 5 GHz and 6GHz wireless connection. Click Apply when done.

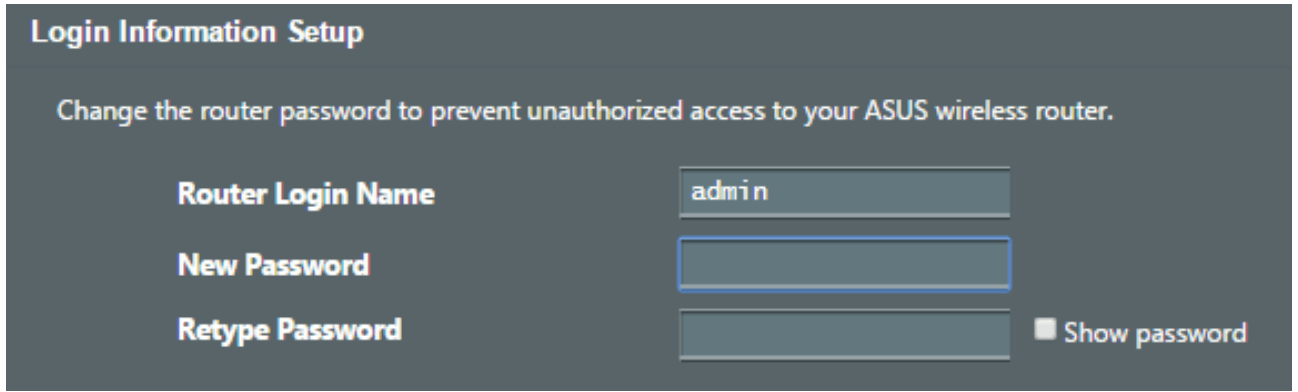
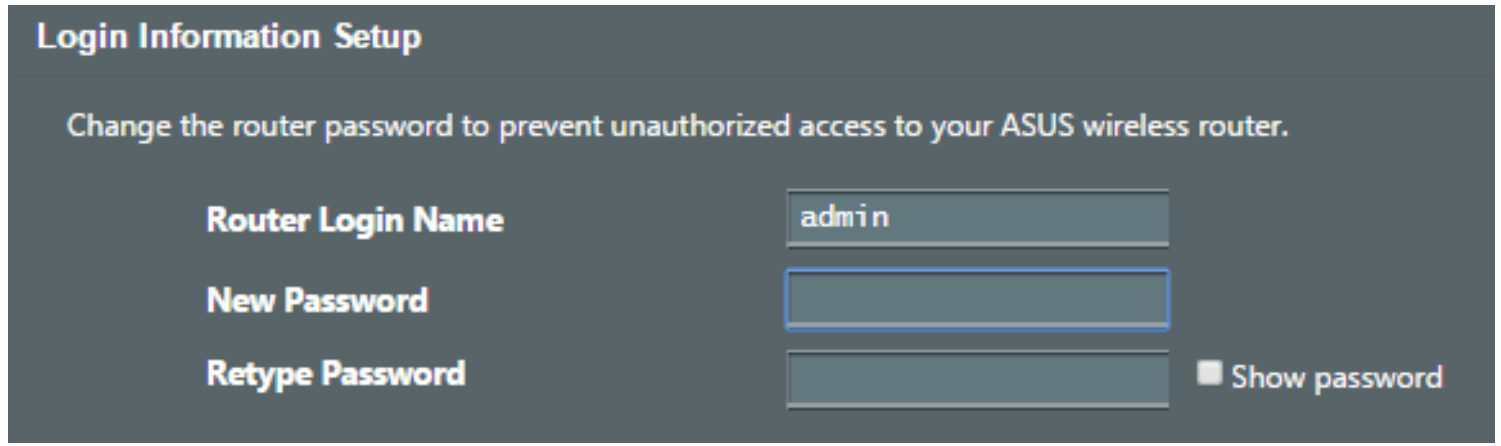
4. On the Login Information Setup page, change the router’s login password to prevent unauthorized access to your wireless router.
NOTE: The wireless router's login username and password is different from the 2.4GHz/5GHz/6GHz network name (SSID) and security key. The wireless router's login username and password allows you to log into your wireless router's Web GUI to configure your wireless router's settings. The 2.4GHz/5GHz/6GHz network name (SSID) and security key allows Wi-Fi devices to log in and connect to your 2.4GHz/5GHz/6GHz network.
Connecting to your wireless network
After setting up your wireless router via QIS, you can connect your computer or other smart devices to your wireless network.
To connect to your network:
1. On your computer, click the network icon  in the notification area to display the available wireless networks.
in the notification area to display the available wireless networks.
2. Select the wireless network that you want to connect to, then click Connect.
3. You may need to key in the network security key for a secured wireless network, then click OK.
4. Wait while your computer establishes connection to the wireless network successfully. The connection status is displayed and the network icon displays the connected status. 
NOTES:
- Refer to the next chapters for more details on configuring your wireless network's settings.
- Refer to your device's user manual for more details on connecting it to your wireless network.
CONFIGURING THE ADVANCED SETTINGS
1. Using the Network Map
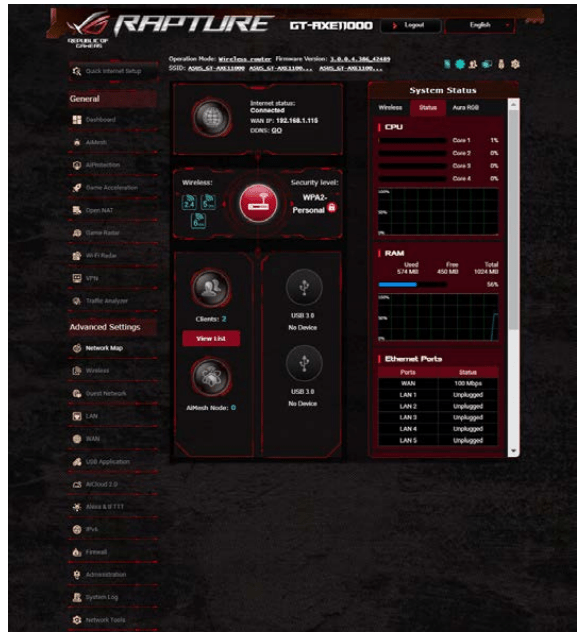
Network Map allows you to configure your network’s security settingstro, manage your network clients, and monitor your USB device.
1.1 Setting up the wireless security settings
To protect your wireless network from unauthorized access, you need to configure its security settings.
To set up the wireless security settings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Network Map.
2. On the Network Map screen and under System status, you can configure the wireless security settings such as SSID, security level, and encryption settings.
NOTE: You can set up different wireless security settings for 2.4GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz bands.
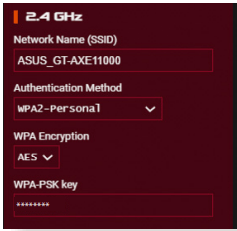
2.4GHz security settings
5GHz security settings
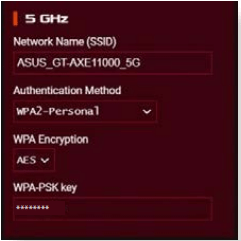
6GHz security settings
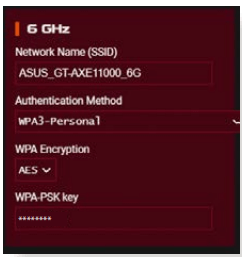
3. On the Wireless name (SSID) field, key in a unique name for your wireless network.
4. From the Authentication Method dropdown list, select the authentication method for your wireless network.
If you select WPA-Personal or WPA-2 Personal as the authentication method, key in the WPA-PSK key or security passkey.
IMPORTANT! The IEEE 802.11n/ac standard prohibits using High Throughput with WEP or WPA-TKIP as the unicast cipher. If you use these encryption methods, your data rate will drop to IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps connection.
5 Click Apply when done.
1.2 Managing your network clients
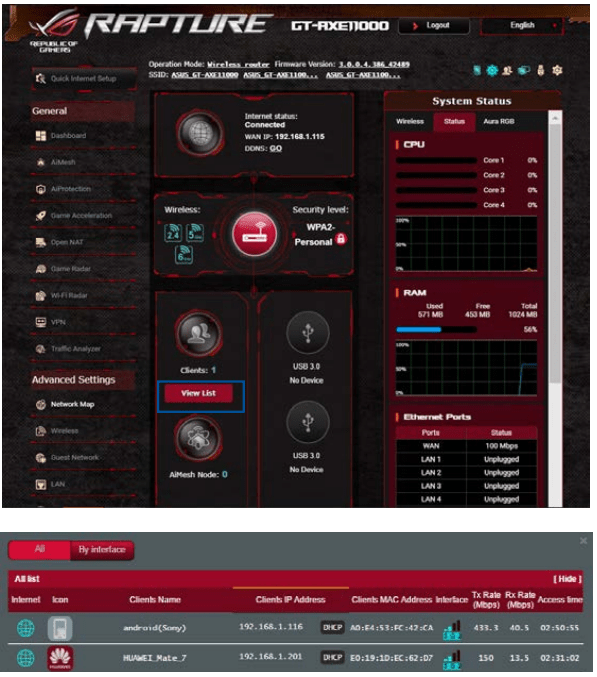
To manage your network clients:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Network Map tab.
2. On the Network Map screen, select the Clients icon to display your network client’s information.
3. Click View List below the Clients icon to display all the clients.
4. To block a client’s access to your network, select the client and click the open lock icon.
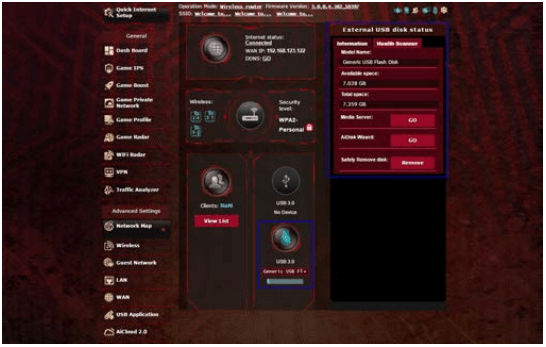
The ASUS wireless router provides two USB ports for connecting USB devices or USB printer to allow you to share files and printer with clients in your network.
NOTES:
- To use this feature, you need to plug a USB storage device, such as a USB hard disk or USB flash drive, to the USB 3.0/2.0 ports on the rear panel of your wireless router. Ensure that the USB storage device is formatted and partitioned properly. Refer to the Plug n-Share Disk Support List at http://event.asus.com/networks/ disksupport
- The USB ports support two USB drives or one printer and one USB drive at the same time.
IMPORTANT! You first need to create a share account and its permission /access rights to allow other network clients to access the USB device via an FTP site/third-party FTP client utility, Servers Center, Samba, or AiCloud. For more details, refer to the section 4.6 Using the USB Application and 4.7 Using AiCloud 2.0 in this user manual.
To monitor your USB device:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Network Map.
2. On the Network Map screen, select the USB Disk Status icon to display your USB device’s information.
3. On the AiDisk Wizard field, click GO to set up an FTP server for Internet file sharing.
NOTES:
- For more details, refer to the section 4.6.2 Using Servers Center in this user manual.
- The wireless router works with most USB HDDs/Flash disks (up to 4TB size) and supports read-write access for FAT16, FAT32, NTFS, and HFS+.
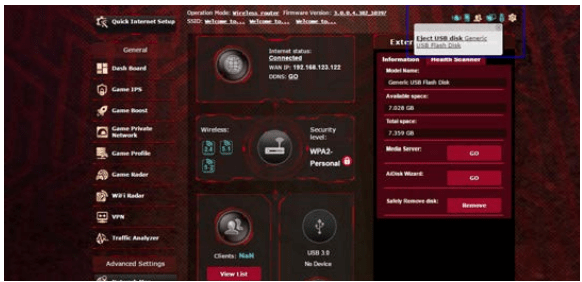
IMPORTANT! Incorrect removal of the USB disk may cause data corruption.
To safely remove the USB disk:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Network Map.
2. In the upper right corner, click > Eject USB disk. When the USB disk is ejected successfully, the USB status shows Unmounted.
1.4.1 Before setting
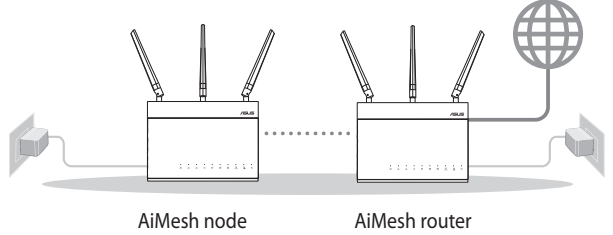
Preparing to setup an AiMesh Wi-Fi system
1. Two (2) ASUS routers (models supporting AiMesh: https://www.asus.com/AiMesh/).
2. Assign one as AiMesh router, and another one as AiMesh node.
NOTE: If you have multiple AiMesh routers, we recommend using the router with the highest specifications as your AiMesh router and the others as AiMesh nodes.
1.4.2 AiMesh Setup steps
Prepare
Place your AiMesh router and node within 1-3 meters of each other during the setup process.
AiMesh node
Factory default status. Keep power on and standby for AiMesh system settings.
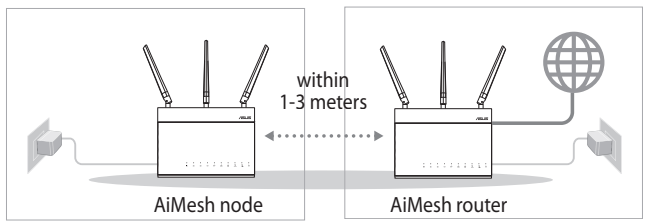
AiMesh router
1) Refer to the other router Quick Start Guide to connect your AiMesh router to your PC and modem, and then log in into the web GUI.
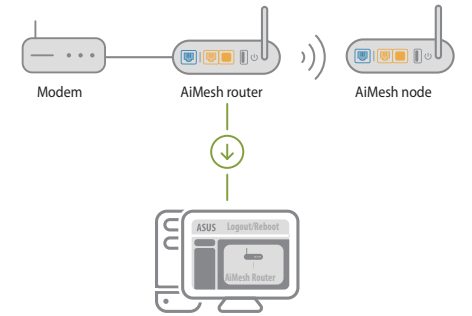
2) Go to Network Map page, click AiMesh icon and then Search for your extending AiMesh node.
NOTE: If you cannot find the AiMesh icon here, click on firmware version and update the firmware.
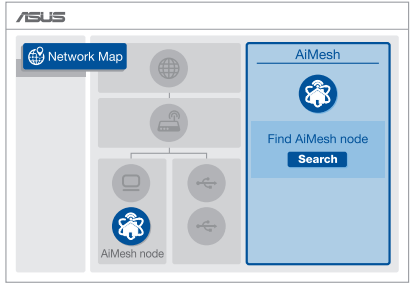
3) Click Search, it will automatically search for your AiMesh node. When the AiMesh node shows on this page, click it to add it into the AiMesh system.
NOTE: If you cannot find any AiMesh node, please go to TROUBLE SHOOTING
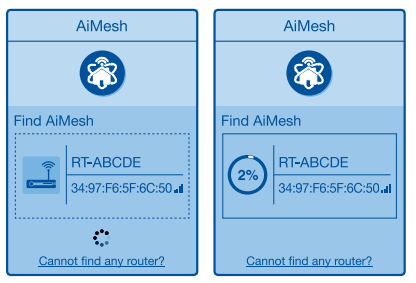
4) A message is displayed when synchronization is completed.

5) Congratulations! You will find the pages below show up when an AiMesh node has been successfully added to the AiMesh network.

1.4.3 Troubleshooting
If your AiMesh router cannot find any AiMesh node nearby or synchronization fails, please check followings and try again.
- Move your AiMesh node closer to the AiMesh router ideally. Ensure it is within 1-3 meters.
- Your AiMesh node is powered on.
- Your AiMesh node is upgraded to AiMesh supported firmware.
- Download AiMesh - supported fireware at: https://www.asus.com/AiMesh/
- Power on your AiMesh node and connect it to your PC via a network cable.
- Launch a web GUI. You will be redirected to the ASUS Setup Wizard. If not, navigate to http://router.asus.com
- Go to Administration > Firmware Upgrade. Click on Choose File, and upload the AiMesh-supported firmware. v. After firmware uploaded, please go to Network Map page to confirm whether AiMesh icon showed up.
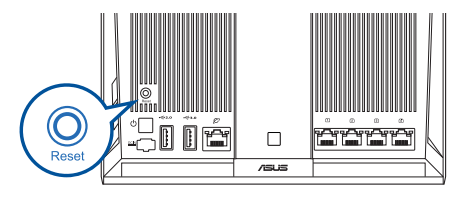
- Press the reset button on your AiMesh node for at least 5 seconds. Release the reset button when the power LED is flashing slowly.

1.4.4 Relocation
The best performance:
Locate your AiMesh node and router at the best place.
NOTES:
- To minimize interference, keep the routers away from devices like cordless phones, Bluetooth devices and microwave ovens.
- We recommend that you place the routers in an open or spacious location.

1.4.5 FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: Does the AiMesh router support Access Point mode?
A: Yes. You can choose to set the AiMesh router as router mode or access point mode. Please go to web GUI (http://router.asus. com), and go to the page Administration > Operation Mode.
Q2: Could I setup wired connection between AiMesh routers (Ethernet backhaul)?
A: Yes. AiMesh system supports both wireless and wired connection between AiMesh router and node to maximize throughput and stability. AiMesh analyzes the wireless signal strength for each frequency band available, and then determines automatically whether a wireless or wired connection is best to serve as the inter-router connection backbone.
1) Follow the setup steps to establish a connection between the AiMesh router and node via Wi-Fi first.
2) Place the node in the ideal locations for best coverage. Run an Ethernet cable from the LAN port of the AiMesh router to the WAN port of AiMesh node.

3) AiMesh system will auto-select the best path for data transmission, whether wired or wireless.
2. Wireless
2.1 General
The General tab allows you to configure the basic wireless settings.
To configure the basic wireless settings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Wireless > General tab.
2. Select 2.4GHz, 5GHz or 6GHz as the frequency band for your wireless network.
3. If you want to use the Smart Connect function, move the slider to ON in the Enable Smart Connect field. This function automatically connect the clients in your network to the appropriate band 2.4GHz, 5GHz or 6GHz for optimal speed.
4. Assign a unique name containing up to 32 characters for your SSID (Service Set Identifier) or network name to identify your wireless network. Wi-Fi devices can identify and connect to the wireless network via your assigned SSID. The SSIDs on the information banner are updated once new SSIDs are saved to the settings.
NOTE: You can assign unique SSIDs for the 2.4 GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz frequency bands.
5. In the Hide SSID field, select Yes to prevent wireless devices from detecting your SSID. When this function is enabled, you would need to enter the SSID manually on the wireless device to access the wireless network.
6. Select any of these wireless mode options to determine the types of wireless devices that can connect to your wireless router:
• Auto: Select Auto to allow 802.11ac, 802.11n, 802.11g, and 802.11b devices to connect to the wireless router.
• N only: Select N only to maximize wireless N performance. This setting prevents 802.11g and 802.11b devices from connecting to the wireless router.
• Legacy: Select Legacy to allow 802.11b/g/n devices to connect to the wireless router. Hardware that supports 802.11n natively, however, will only run at a maximum speed of 54Mbps.
7. Select the operating/control channel for your wireless router. Select Auto to allow the wireless router to automatically select the channel that has the least amount of interference.
8. Select the channel bandwidth to accommodate higher transmission speeds.
9. Select the authentication method.
10.When done, click Apply.
2.2 WPS
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) is a wireless security standard that allows you to easily connect devices to a wireless network. You can configure the WPS function via the PIN code or WPS button.
NOTE: Ensure that the devices support WPS.
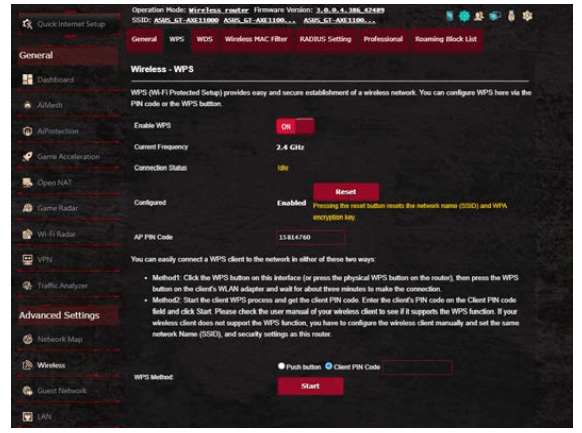
To enable WPS on your wireless network:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Wireless > WPS tab.
2. In the Enable WPS field, move the slider to ON.
3. WPS uses 2.4GHz by default. If you want to change the frequency to 5GHz, turn OFF the WPS function, click Switch Frequency in the Current Frequency field, and turn WPS ON again.
NOTE: WPS supports authentication using Open System, WPA Personal, and WPA2-Personal. WPS does not support a wireless network that uses a Shared Key, WPA-Enterprise, WPA2-Enterprise, and RADIUS encryption method.
4. In the WPS Method field, select Push Button or Client PIN code. If you select Push Button, go to step 5. If you select Client PIN code, go to step 6.
5. To set up WPS using the router’s WPS button, follow these steps:
a.Click Start or press the WPS button found at the rear of the wireless router.
b.Press the WPS button on your wireless device. This is normally identified by the WPS logo.
NOTE: Check your wireless device or its user manual for the location of the WPS button.
c. The wireless router will scan for any available WPS devices. If the wireless router does not find any WPS devices, it will switch to standby mode.
6. To set up WPS using the Client’s PIN code, follow these steps:
a. Locate the WPS PIN code on your wireless device’s user manual or on the device itself.
b.Key in the Client PIN code on the text box.
c. Click Start to put your wireless router into WPS survey mode. The router’s LED indicators quickly flash three times until the WPS setup is completed.
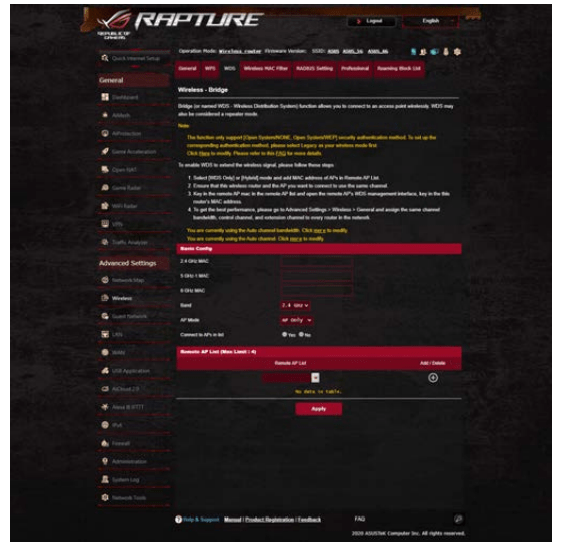
2.3 Bridge
Bridge or WDS (Wireless Distribution System) allows your ASUS wireless router to connect to another wireless access point exclusively, preventing other wireless devices or stations to access your ASUS wireless router. It can also be considered as a wireless repeater where your ASUS wireless router communicates with another access point and other wireless devices.

To set up the wireless bridge:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Wireless > WDS tab.
2. Select the frequency band for the wireless bridge.
3. In the AP Mode field, select any of these options: • AP Only: Disables the Wireless Bridge function.
• WDS Only: Enables the Wireless Bridge feature but prevents other wireless devices/stations from connecting to the router.
• HYBRID: Enables the Wireless Bridge feature and allows other wireless devices/stations to connect to the router.
NOTE: In Hybrid mode, wireless devices connected to the ASUS wireless router will only receive half the connection speed of the Access Point.
4. In the Connect to APs in list field, click Yes if you want to connect to an Access Point listed in the Remote AP List.
5. By default, the operating/control channel for the wireless bridge is set to Auto to allow the router to automatically select the channel with the least amount of interference.
You can modify the Control Channel from Advanced Settings > Wireless > General tab.
NOTE: Channel availability varies per country or region.
6. On the Remote AP List, key in a MAC address and click the Add button  to enter the MAC address of other available Access Points.
to enter the MAC address of other available Access Points.
NOTE: Any Access Point added to the list should be on the same Control Channel as the ASUS wireless router.
7. Click Apply.
2.4 Wireless MAC Filter
Wireless MAC filter provides control over packets transmitted to a specified MAC (Media Access Control) address on your wireless network.
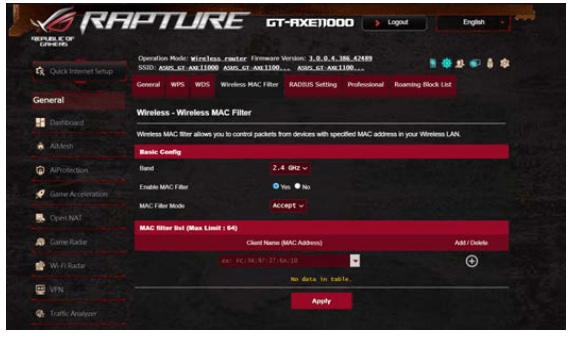
To set up the Wireless MAC filter:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Wireless > Wireless MAC Filter tab.
2. Select the frequency band.
3. Tick Yes in the Enable Mac Filter field.
4. In the MAC Filter Mode dropdown list, select either Accept or Reject.
• Select Accept to allow devices in the MAC filter list to access to the wireless network.
• Select Reject to prevent devices in the MAC filter list to access to the wireless network.
5. On the MAC filter list, click the Add button  and key in the MAC address of the wireless device.
and key in the MAC address of the wireless device.
6. Click Apply.
2.5 RADIUS Setting
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service) Setting provides an extra layer of security when you choose WPA Enterprise, WPA2-Enterprise, or Radius with 802.1x as your Authentication Mode.
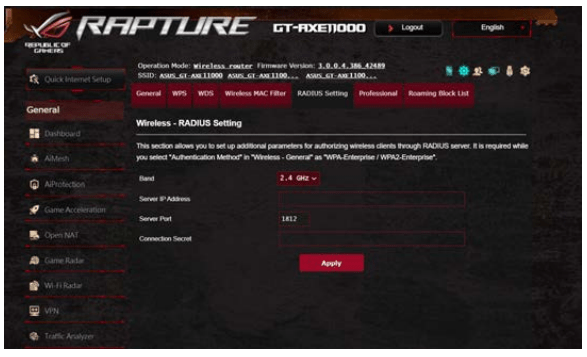
To set up wireless RADIUS settings:
1. Ensure that the wireless router’s authentication mode is set to WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise.
NOTE: Please refer to section 4.2.1 General for configuring your wireless router’s Authentication Mode.
2. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Wireless > RADIUS Setting.
3. Select the frequency band.
4. In the Server IP Address field, key in your RADIUS server’s IP Address.
5. In the Server Port field, key in the server port.
6. In the Connection Secret field, assign the password to access your RADIUS server.
7. Click Apply.
2.6 Professional
The Professional screen provides advanced configuration options. NOTE: We recommend that you use the default values on this page.
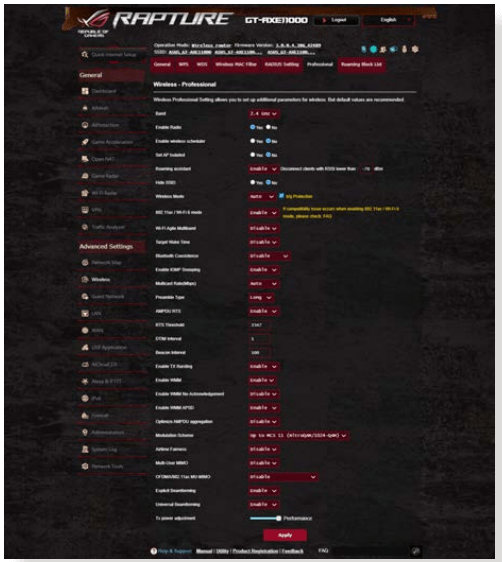
In the Professional Settings screen, you can configure the following:
- Frequency: Select the frequency band that the professional settings will be applied to.
- Enable Radio: Select Yes to enable wireless networking. Select No to disable wireless networking.
- Enable wireless scheduler: Select Yes to enable and configure wireless scheduler. Select No to disable wireless scheduler.
- Date to Enable Radio (weekdays): You can specify which days of the week wireless networking is enabled.
- Time of Day to Enable Radio: You can specify a time range when wireless networking is enabled during the week.
- Date to Enable Radio (weekend): You can specify which days of the weekend wireless networking is enabled.
- Time of Day to Enable Radio: You can specify a time range when wireless networking is enabled during the weekend.
- Set AP isolated: The Set AP isolated item prevents wireless devices on your network from communicating with each other. This feature is useful if many guests frequently join or leave your network. Select Yes to enable this feature or select No to disable.
- Roaming Assistant: In network configurations that involve multiple Access, Points or wireless repeater, wireless clients sometimes cannot connect automatically to thefts available AP because they are still connected to the main wireless router. Enable this setting so that the client will disconnect from the main wireless router if the signal strength is under a specific threshold and connect to a stronger signal.
- Enable IGMP Snooping: Enable this function allows the IGMP ( Internet Group Management Protocol ) to be monitored among devices and optimizes wireless multicast traffic.
- Multicast Rate (Mbps): Select the multicast transmission rate or click Disable to switch off simultaneous single transmission.
- Preamble Type: Preamble Type defines the length of time that the router spent for CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check). CRC is a method of detecting errors during data transmission. Select Short for a busy wireless network with high network traffic. Select Long if your wireless network is composed of older or legacy wireless devices.
- AMPDU RTS: Enable this function allows to build a group of frames before they are transmitted and use RTS for every AMPDU for communication among 802.11g and 802.11b devices.
- RTS Threshold: Select a lower value for RTS (Request to Send) Threshold to improve wireless communication in a busy or noisy wireless network with high network traffic and numerous wireless devices.
- DTIM Interval: DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) Interval or Data Beacon Rate is the time interval before a signal is sent to a wireless device in sleep mode indicating that a data packet is awaiting delivery. The default value is three milliseconds.
- Beacon Interval: Beacon Interval is the time between one DTIM and the next. The default value is 100 milliseconds. Lower the Beacon Interval value for an unstable wireless connection or for roaming devices.
- Enable TX Bursting: Enable TX Bursting improves transmission speed between the wireless router and 802.11g devices.
- Enable WMM APSD: Enable WMM APSD (Wi-Fi Multimedia Automatic Power Save Delivery) to improve power management between wireless devices. Select Disable to switch off WMM APSD.
- Reducing USB 3.0 interference: Enable this function ensures the best wireless performance on the 2.4 GHz band. Disabling this feature increase USB 3.0 port’s transmission speed and may affect the 2.4 GHz wireless range.
- Optimize AMPDU aggregation: Optimize the max number of MPDUs in an AMPDU and avoid packets get lost or corrupted during transmission in error-prone wireless channels
- Turbo QAM: Enable this function allows to support 256-QAM (MCS 8/9) on the 2.4GHz band to achieve better range and throughput on that frequency.
- Airtime Fairness: With airtime fairness, the speed of the network is not determined by the slowest traffic. By allocating time equally among clients, Airtime Fairness allows every transmission to move at its highest potential speed.
- Explicit Beamforming: The client’s WLAN adapter and router both support beam forming technology. This technology allows these device to communicate the channel estimation and steering direction to each other to improve download and uplink speed.
- Universal Beamforming: For legacy wireless network adapter that do not support beam forming, the router estimates the channel and determines the steering direction to improve the downlink speed.
3. Creating a Guest Network
The Guest Network provides temporary visitors with Internet connectivity via access to separate SSIDs or networks without providing access to your private network.
NOTE: GT-AXE11000 supports up to nine SSIDs (three 2.4GHz, three 5GHz and three 6GHz).
To create a guest network:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Guest Network.
2. On the Guest Network screen, select 2.4Ghz, 5Ghz or 6GHz frequency band for the guest network that you want to create.
3. Click Enable.
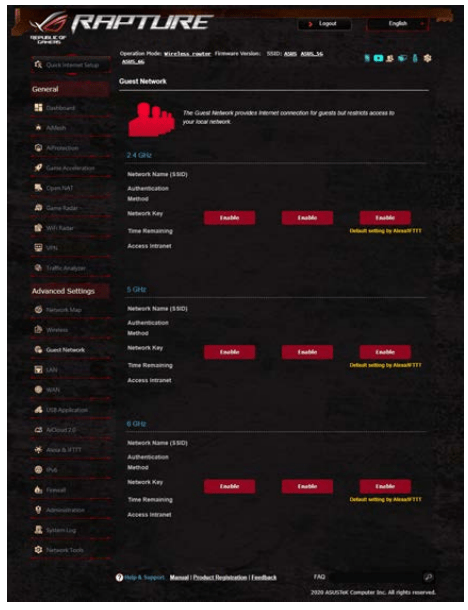
4. To change a guest’s settings, click the guest settings you want to modify. Click Remove to delete the guest’s settings.
5. Assign a wireless name for your temporary network on the Network Name (SSID) field.
6. Select an Authentication Method.
7. If you select a WPA authentication method, select a WPA Encryption.
8. Specify the Access time or choose Limitless.
9. Select Disable or Enable on the Access Intranet item. 10.When done, click Apply.
4. LAN
4.1 LAN IP
The LAN IP screen allows you to modify the LAN IP settings of your wireless router.
NOTE: Any changes to the LAN IP address will be reflected on your DHCP settings.
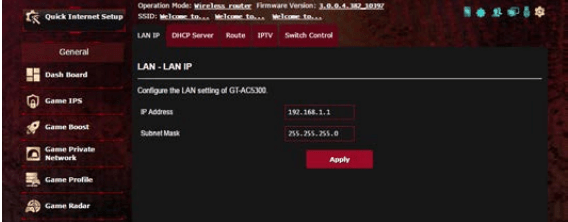
To modify the LAN IP settings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > LAN > LAN IP tab.
2. Modify the IP address and Subnet Mask.
3. When done, click Apply.
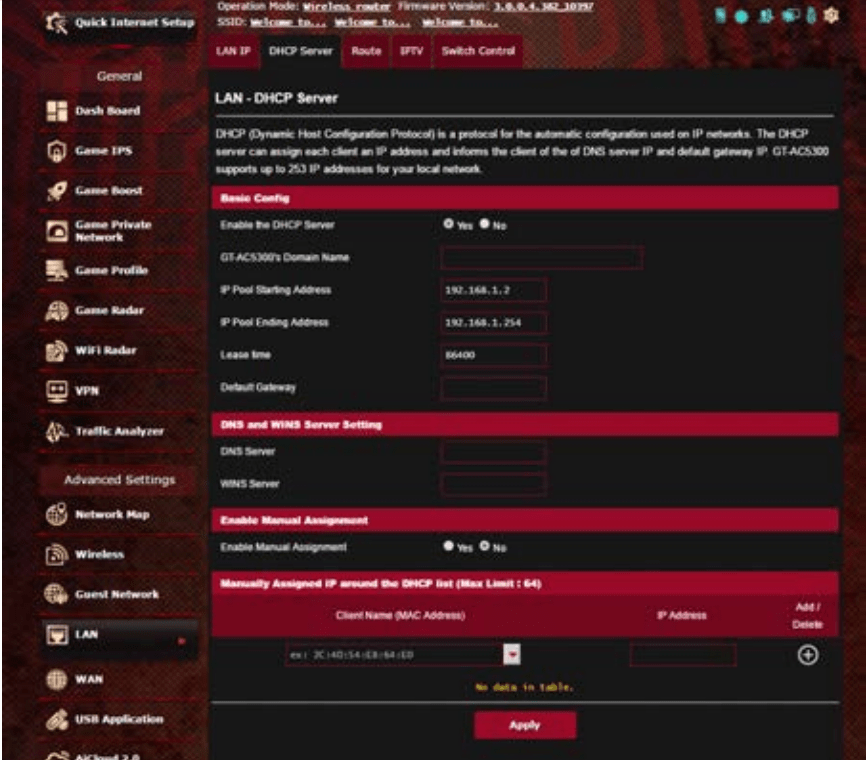
4.2 DHCP Server
Your wireless router uses DHCP to assign IP addresses automatically on your network. You can specify the IP address range and lease time for the clients on your network.
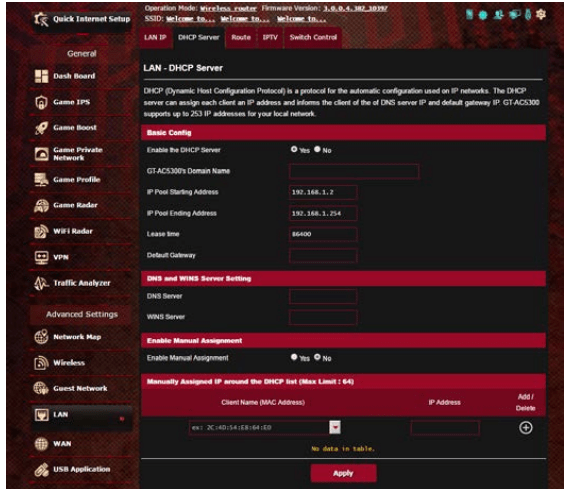
To configure the DHCP server:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > LAN > DHCP Server tab.
2. In the Enable the DHCP Server field, tick Yes.
3. In the Domain Name text box, enter a domain name for the wireless router.
4. In the IP Pool Starting Address field, key in the starting IP address.
5. In the IP Pool Ending Address field, key in the ending IP address.
6. In the Lease Time field, specify in seconds when an assigned IP address will expire. Once it reaches this time limit, the DHCP server will then assign a new IP address.
NOTES:
- We recommend that you use an IP address format of 192.168.1.xxx (where xxx can be any number between 2 and 254) when specifying an IP address range.
- An IP Pool Starting Address should not be greater than the IP Pool Ending Address.
7. In the DNS and Server Settings section, key in your DNS Server and WINS Server IP address if needed.
8. Your wireless router can also manually assign IP addresses to devices on the network. On the Enable Manual Assignment field, choose Yes to assign an IP address to specific MAC addresses on the network. Up to 32 MAC Addresses can be added to the DHCP list for manual assignment.
4.3 Route
If your network makes use of more than one wireless router, you can configure a routing table to share the same Internet service.
NOTE: We recommend that you do not change the default route settings unless you have advanced knowledge of routing tables.
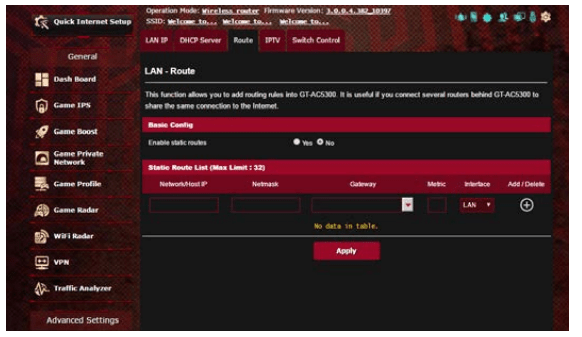
To configure the LAN Routing table:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > LAN > Route tab.
2. On the Enable static routes field, choose Yes.
3. On the Static Route List, enter the network information of other access points or nodes. Click the Add  or Delete
or Delete button to add or remove a device on the list.
button to add or remove a device on the list.
4. Click Apply.
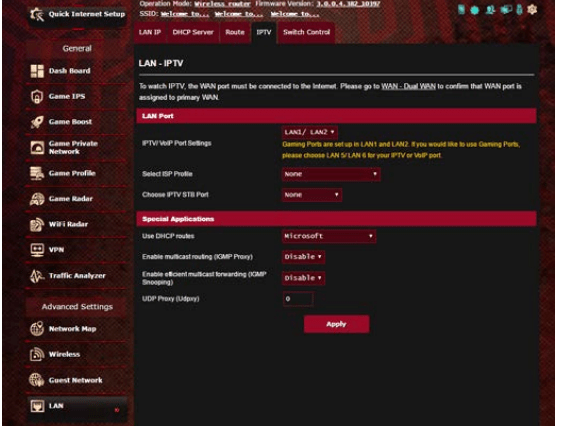
4.4 IPTV
The wireless router supports connection to IPTV services through an ISP or a LAN. The IPTV tab provides the configuration settings needed to set up IPTV, VoIP, multicasting, and UDP for your service. Contact your ISP for specific information regarding your service.
5. WAN
5.1 Internet Connection
The Internet Connection screen allows you to configure the settings of various WAN connection types.
To configure the WAN connection settings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > WAN > Internet Connection tab.
2. Configure the following settings below. When done, click Apply.
- WAN Connection Type: Choose your Internet Service Provider type. The choices are Automatic IP, PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP or static IP. Consult your ISP if the router is unable to obtain a valid IP address or if you are unsure the WAN connection type.
- Enable WAN: Select Yes to allow the router Internet access. Select No to disable Internet access.
- Enable NAT: NAT (Network Address Translation) is a system where one public IP (WAN IP) is used to provide Internet access to network clients with a private IP address in a LAN. The private IP address of each network client is saved in a NAT table and is used to route incoming data packets.
- Enable UPnP: UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) allows several devices (such as routers, televisions, stereo systems, game consoles, and cellular phone), to be controlled via an IP-based network with or without a central control through a gateway. UPnP connects PCs of all form factors, providing a seamless network for remote configuration and data transfer. Using UPnP, a new network device is discovered automatically. Once connected to the network, devices can be remotely configured to support P2P applications, interactive gaming, video conferencing, and web or proxy servers. Unlike Port forwarding, which involves manually configuring port settings, UPnP automatically configures the router to accept incoming connections and direct requests to a specific PC on the local network.
- Connect to DNS Server automatically: Allows this router to get the DNS IP address from the ISP automatically. A DNS is a host on the Internet that translates Internet names to numeric IP addresses.
- Authentication: This item may be specified by some ISPs. Check with your ISP and fill them in if required.
- Host Name: This field allows you to provide a host name for your router. It is usually a special requirement from your ISP. If your ISP assigned a host name to your computer, enter the host name here.
- Enable WAN: Select Yes to allow the router Internet access. Select No to disable Internet access.
- Enable NAT: NAT (Network Address Translation) is a system where one public IP (WAN IP) is used to provide Internet access to network clients with a private IP address in a LAN. The private IP address of each network client is saved in a NAT table and is used to route incoming data packets.
- Enable UPnP: UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) allows several devices (such as routers, televisions, stereo systems, game consoles, and cellular phone), to be controlled via an IP-based network with or without a central control through a gateway. UPnP connects PCs of all form factors, providing a seamless network for remote configuration and data transfer. Using UPnP, a new network device is discovered automatically. Once connected to the network, devices can be remotely configured to support P2P applications, interactive gaming, video conferencing, and web or proxy servers. Unlike Port forwarding, which involves manually configuring port settings, UPnP automatically configures the router to accept incoming connections and direct requests to a specific PC on the local network.
- Connect to DNS Server automatically: Allows this router to get the DNS IP address from the ISP automatically. A DNS is a host on the Internet that translates Internet names to numeric IP addresses.
- Authentication: This item may be specified by some ISPs. Check with your ISP and fill them in if required.
- Host Name: This field allows you to provide a host name for your router. It is usually a special requirement from your ISP. If your ISP assigned a host name to your computer, enter the host name here.
- MAC Address: MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier for your networking device. Some ISPs monitor the MAC address of networking devices that connect to their service and reject any unrecognized device that attempt to connect. To avoid connection issues due to an unregistered MAC address, you can:
- Contact your ISP and update the MAC address associated with your ISP service.
- Clone or change the MAC address of the ASUS wireless router to match the MAC address of the previous networking device recognized by the ISP.
- DHCP query frequency: Changes the DHCP Discovery interval settings to avoid overloading the DHCP server.
5.2 Dual WAN
Your ASUS wireless router provides dual WAN support. You can set the dual WAN feature to any of these two modes:
- Failover Mode: Select this mode to use the secondary WAN as the backup network access.
- Load Balance Mode: Select this mode to optimize bandwidth, minimize response time and prevent data overload for both primary and secondary WAN connections.
5.3 Port Trigger
Port range triggering opens a predetermined incoming port for a limited period of time whenever a client on the local area network makes an outgoing connection to a specified port. Port triggering is used in the following scenarios:
- More than one local client needs port forwarding for the same application at a different time.
- An application requires specific incoming ports that are different from the outgoing ports.
To set up Port Trigger:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > WAN > Port Trigger tab.
- On the Enable Port Trigger field, tick Yes.
- On the Well-Known Applications field, select the popular games and web services to add to the Port Trigger List.
- On the Trigger Port List table, key in the following information:
- Description: Enter a short name or description for the service.
- Trigger Port: Specify a trigger port to open the incoming port.
- Protocol: Select the protocol, TCP, or UDP.
- Incoming Port: Specify an incoming port to receive inbound data from the Internet.
- Protocol: Select the protocol, TCP, or UDP.
- Click the Add
 to enter the port trigger information to the list. Click the Delete
to enter the port trigger information to the list. Click the Delete button to remove a port trigger entry from the list.
button to remove a port trigger entry from the list. - When done, click Apply.
NOTES:
- When connecting to an IRC server, a client PC makes an outgoing connection using the trigger port range 66660-7000. The IRC server responds by verifying the username and creating a new connection to the client PC using an incoming port.
- If Port Trigger is disabled, the router drops the connection because it is unable to determine which PC is requesting for IRC access. When Port Trigger is enabled, the router assigns an incoming port to receive the inbound data. This incoming port closes once a specific time period has elapsed because the router is unsure when the application has been terminated.
- Port triggering only allows one client in the network to use a particular service and a specific incoming port at the same time.
- You cannot use the same application to trigger a port in more than one PC at the same time. The router will only forward the port back to the last computer to send the router a request/ trigger.
5.4 Virtual Server/Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is a method to direct network traffic from the Internet to a specific port or a specific range of ports to a device or number of devices on your local network. Setting up Port Forwarding on your router allows PCs outside the network to access specific services provided by a PC in your network.
To set up Port Forwarding:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > WAN > Virtual Server / Port Forwarding tab.
- On the Enable Port Forwarding field, tick Yes.
- On the Famous Server List field, select the type of service you want to access.
- On the Famous Game List field, select the popular game that you want to access. This item lists the port required for your selected popular online game to work properly.
- On the Port Forwarding List table, key in the following information:
- Service Name: Enter a service name.
- Port Range: If you want to specify a Port Range for clients on the same network, enter the Service Name, the Port Range (e.g. 10200:10300), the LAN IP address, and leave the Local Port empty. Port range accepts various formats such as Port Range (300:350), individual ports (566,789) or Mix (1015:1024,3021).
NOTES:
- When your network’s firewall is disabled and you set 80 as the HTTP server’s port range for your WAN setup, then your http server/web server would be in conflict with the router’s web user interface.
- A network makes use of ports in order to exchange data, with each port assigned a port number and a specific task. For example, port 80 is used for HTTP. A specific port can only be used by one application or service at a time. Hence, two PCs attempting to access data through the same port at the same time would fail. For example, you cannot set up Port Forwarding for port 100 for two PCs at the same time.
- Local IP: Key in the client’s LAN IP address.
NOTE: Use a static IP address for the local client to make port forwarding work properly. Refer to section 4.4 LAN for information.
- Local Port: Enter a specific port to receive forwarded packets. Leave this field blank if you want the incoming packets to be redirected to the specified port range.
- Protocol: Select the protocol. If you are unsure, select BOTH.
6. Click the Add  to enter the port trigger information to the list. Click the Delete
to enter the port trigger information to the list. Click the Delete button to remove a port trigger entry from the list.
button to remove a port trigger entry from the list.
7. When done, click Apply.
To check if Port Forwarding has been configured successfully:
- Ensure that your server or application is set up and running.
- You will need a client outside your LAN but has Internet access (referred to as “Internet client”). This client should not be connected to the ASUS router.
- On the Internet client, use the router’s WAN IP to access the server. If port forwarding has been successful, you should be able to access the files or applications.
Differences between port trigger and port forwarding:
- Port triggering will work even without setting up a specific LAN IP address. Unlike port forwarding, which requires a static LAN IP address, port triggering allows dynamic port forwarding using the router. Predetermined port ranges are configured to accept incoming connections for a limited period of time. Port triggering allows multiple computers to run applications that would normally require manually forwarding the same ports to each PC on the network.
- Port triggering is more secure than port forwarding since the incoming ports are not open all the time. They are opened only when an application is making an outgoing connection through the trigger port.
5.5 DMZ
Virtual DMZ exposes one client to the Internet, allowing this client to receive all inbound packets directed to your Local Area Network.
Inbound traffic from the Internet is usually discarded and routed to a specific client only if port forwarding or a port trigger has been configured on the network. In a DMZ configuration, one network client receives all inbound packets.
Setting up DMZ on a network is useful when you need incoming ports open or you want to host a domain, web, or e-mail server.
CAUTION: Opening all the ports on a client to the Internet makes the network vulnerable to outside attacks. Please be aware of the security risks involved in using DMZ.
To set up DMZ:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > WAN > DMZ tab.
- Configure the setting below. When done, click Apply.
• IP address of Exposed Station: Key in the client’s LAN IP address that will provide the DMZ service and be exposed on the Internet. Ensure that the server client has a static IP address.
To remove DMZ:
- Delete the client’s LAN IP address from the IP Address of Exposed Station text box.
- When done, click Apply.
5.6 DDNS
Setting up DDNS (Dynamic DNS) allows you to access the router from outside your network through the provided ASUS DDNS Service or another DDNS service.
To set up DDNS:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > WAN > DDNS tab.
- Configure the following settings below. When done, click Apply.
- Enable the DDNS Client: Enable DDNS to access the ASUS router via the DNS name rather than WAN IP address.
- Server and Host Name: Choose ASUS DDNS or other DDNS. If you want to use ASUS DDNS, fill in the Host Name in the format of xxx.asuscomm.com (xxx is your host name).
- If you want to use a different DDNS service, click FREE TRIAL and register online first. Fill in the User Name or E-mail Address and Password or DDNS Key fields.
- Enable wildcard: Enable wildcard if your DDNS service requires one.
NOTES: DDNS service will not work under these conditions:
- When the wireless router is using a private WAN IP address (192.168.x.x, 10.x.x.x, or 172.16.x.x), as indicated by a yellow text.
- The router may be on a network that uses multiple NAT tables.
5.7 NAT Passthrough
NAT Passthrough allows a Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection to pass through the router to the network clients. PPTP Passthrough, L2TP Passthrough, IPsec Passthrough and RTSP Passthrough are enabled by default.
To enable / disable the NAT Passthrough settings, go to the Advanced Settings > WAN > NAT Passthrough tab. When done, click Apply.
6. Using the USB Application
The USB Applications function provides AiDisk, Servers Center, Network Printer Server and Download Master submenus.
IMPORTANT! To use the server functions, you need to insert a USB storage device, such as a USB hard disk or USB flash drive, in the USB 3.0 port on the rear panel of your wireless router. Ensure that the USB storage device is formatted and partitioned properly. Refer to the ASUS website at http://event.asus.com/2009/networks/disksupport/ for the file system support table.
6.1 Using AiDisk
AiDisk allows you to share files stored on a connected USB device through the Internet. AiDisk also assists you with setting up ASUS DDNS and an FTP server.
To use AiDisk:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > USB Application, then click the AiDisk icon.
2. From the Welcome to AiDisk wizard screen, click Go.
3. Select the access rights that you want to assign to the clients accessing your shared data.
4. Create your domain name via the ASUS DDNS services, read the Terms of Service and then select I will use the service and accept the Terms of service and key in your domain name. When done, click Next.
You can also select Skip ASUS DDNS settings then click Next to skip the DDNS setting.
5. Click Finish to complete the setting.
6. To access the FTP site that you created, launch a web browser or a third-party FTP client utility and key in the ftp link (ftp://.asuscomm.com) you have previously created.
6.2 Using Servers Center
Servers Center allows you to share the media files from the USB disk via a Media Server directory, Samba share service, or FTP share service. You can also configure other settings for the USB disk in the Servers Center.
Using Media Server
Your wireless router allows DLNA-supported devices to access multimedia files from the USB disk connected to your wireless router.
NOTE: Before using the DLNA Media Server function, connect your device to the router’s network.
To launch the Media Server setting page, go to Advanced Settings > USB Application > Media Servers tab. Refer to the following for the descriptions of the fields:
- Enable iTunes Server?: Select ON/OFF to enable/disable the iTunes Server.
- Enable UPnP Media Server: Select ON/OFF to enable/ disable the DLNA Media Server.
- Media Server Status: Displays the status of the media server.
- Media Server Path Setting: Select All Disks Shared or Manual Media Server Path.
Using Network Place (Samba) Share service
Network Place (Samba) Share allows you to set up the accounts and permissions for the Samba service.
To use Samba share:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > USB Application > Network Place (Samba) Share / Cloud Disk tab.
NOTE: Network Place (Samba) Share is enabled by default.
2. Follow the steps below to add, delete, or modify an account.
To create a new account:
a. Click  to add new account.
to add new account.
b. In the Account and Password fields, key in the name and password of your network client. Retype the password to confirm. Click Add to add the account to the list.
To delete an existing account:
- Select the account that you want to delete.
- Click
 .
. - When prompted, click Delete to confirm the account deletion.
To add a folder:
a. Click  .
.
b. Enter the folder name, and click Add. The folder that you created will be added to the folder list.
3. From the list of folders, select the type of access permission that you want to assign for specific folders:
- R/W: Select this option to assign read/write access.
- R: Select this option to assign read-only access.
- No: Select this option if you do not want to share a specific file folder.
4. Click Apply to apply the changes.
Using the FTP Share service
FTP share enables an FTP server to share files from USB disk to other devices via your local area network or via the Internet.
IMPORTANT!
- Ensure that you safely remove the USB disk. Incorrect removal of the USB disk may cause data corruption.
- To safely remove the USB disk, refer to the section Safely removing the USB disk under
4.1.3 Monitoring your USB device.
To use FTP Share service:
NOTE: Ensure that you have set up your FTP server through AiDisk. For more details, refer to the section 4.6.1 Using AiDisk.
- From the navigation panel, click Advanced Settings > USB Application > FTP Share tab.
- From the list of folders, select the type of access rights that you want to assign for specific folders:
- R/W: Select to assign read/write access for a specific folder.
- W: Select to assign write only access for a specific folder.
- R: Select to assign read only access for a specific folder.
- No: Select this option if you do not want to share a specific folder.
- If you prefer, you can set the Allow anonymous login field to ON.
- In the Maximum number of concurrent connections field, key in the number of devices that can simultaneously connect to the FTP share server.
- Click Apply to confirm the changes.
- To access the FTP server, key in the ftp link ftp://.asuscomm.com and your user name and password on a web browser or a third-party FTP utility.
6.3 3G/4G
3G/4G USB modems can be connected to the router to allow Internet access.
NOTE: For a list of verified USB modems, please visit: http://event.asus.com/2009/networks/3gsupport/
To set up 3G/4G internet access:
- From the navigation panel, click Advanced Settings > USB application > 3G/4G.
- In the Enable USB Modem field, select Yes.
- Set up the following:
- Location: Select your 3G/4G service provider’s location from the dropdown list.
- ISP: Select your Internet Service Provider (ISP) from the dropdown list.
- APN (Access Point Name) service (optional): Contact your 3G/4G service provider for detailed information.
- Dial Number and PIN code: The 3G/4G provider’s access number and PIN code for connection.
NOTE: PIN code may vary from different providers.
- Username / Password: The username and password will be provided by the 3G/4G network carrier.
- USB Adapter: Choose your USB 3G / 4G adapter from the dropdown list. If you are not sure of your USB adapter’s model or the model is not listed in the options, select Auto.
4. Click Apply.
NOTE: The router will reboot for the settings to take effect.
7. Using AiCloud 2.0
AiCloud 2.0 is a cloud service application that allows you to save, sync, share, and access your files.
To use AiCloud:
- From Google Play Store or Apple Store, download and install the ASUS AiCloud app to your smart device.
- Connect your smart device to your network. Follow the instructions to complete the AiCloud setup process.
7.1 Cloud Disk
To create a cloud disk:
- Insert a USB storage device into the wireless router.
- Turn on Cloud Disk.
- Go to https://router.asus.com and enter the router login account and password. For better user experience, we recommend that you use Google Chrome or Firefox.
- You can now start accessing Cloud Disk files on devices connected to the network.
NOTE: When accessing the devices that are connected to the network, you need to enter the device’s user name and password manually, which will not be saved by AiCloud for security reason.
7.2 Smart Access
The Smart Access function allows you to easily access your home network via your router’s domain name.
NOTES:
- You can create a domain name for your router with ASUS DDNS. For more details, refer to section 4.5.6 DDNS.
- By default, AiCloud provides a secure HTTPS connection. Key in https://[yourASUSDDNSname].asuscomm.com for a very secure Cloud Disk and Smart Access usage.
7.3 AiCloud Sync
To use AiCloud Sync:
- Launch AiCloud, click AiCloud Sync > Go.
- Select ON to enable AiCloud Sync.
- Click Add new account.
- Enter your ASUS WebStorage account password and select the directory that you want to sync with WebStorage.
- Click Apply.
8. IPv6
This wireless router supports IPv6 addressing, a system that supports more IP addresses. This standard is not yet widely available. Contact your ISP if your Internet service supports IPv6.
To set up IPv6:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > IPv6.
- Select your Connection Type. The configuration options vary depending on your selected connection type.
- Enter your IPv6 LAN and DNS settings.
- Click Apply.
NOTE: Please refer to your ISP regarding specific IPv6 information for your Internet service.
9. Firewall
The wireless router can serve as a hardware firewall for your network.
NOTE: The Firewall feature is enabled by default.
9.1 General
To set up basic Firewall settings:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Firewall > General tab.
- On the Enable Firewall field, select Yes.
- On the Enable DoS protection, select Yes to protect your network from DoS (Denial of Service) attacks though this may affect your router’s performance.
- You can also monitor packets exchanged between the LAN and WAN connection. On the Logged packets type, select Dropped, Accepted, or Both.
- Click Apply.
9.2 URL Filter
You can specify keywords or web addresses to prevent access to specific URLs.
NOTE: The URL Filter is based on a DNS query. If a network client has already accessed a website such as http://www.abcxxx.com, then the website will not be blocked (a DNS cache in the system stores previously visited websites). To resolve this issue, clear the DNS cache before setting up the URL Filter.
To set up a URL filter:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Firewall > URL Filter tab.
- On the Enable URL Filter field, select Enabled.
- Enter a URL and click the button.
- Click Apply.
9.3. Keyword filter
Keyword filter blocks access to webpages containing specified keywords.
To set up a keyword filter:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Firewall > Keyword Filter tab.
- On the Enable Keyword Filter field, select Enabled.
- Enter a word or phrase and click the
 button.
button. - Click Apply.
NOTES:
- The Keyword Filter is based on a DNS query. If a network client has already accessed a website such as http://www.abcxxx.com, then the website will not be blocked (a DNS cache in the system stores previously visited websites). To resolve this issue, clear the DNS cache before setting up the Keyword Filter.
- Web pages compressed using HTTP compression cannot be filtered. HTTPS pages also cannot be blocked using a keyword filter.
9.4. Network Services Filter
The Network Services Filter blocks LAN to WAN packet exchanges and restricts network clients from accessing specific web services such as Telnet or FTP.
To set up a Network Service filter:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Firewall > Network Service Filter tab.
- On the Enable Network Services Filter field, select Yes.
- Select the Filter table type. Black List blocks the specified network services. White List limits access to only the specified network services.
- Specify the day and time when the filters will be active.
- To specify a Network Service to filter, enter the Source IP, Destination IP, Port Range, and Protocol. Click the button.
- Click Apply.
9.5 IPv6 Firewall
By default, your ASUS wireless router blocks all unsolicited incoming traffic. The IPv6 Firewall function allows incoming traffic coming from specified services to go through your network.
10. Administration10.1 Operation Mode
The Operation Mode page allows you to select the appropriate mode for your network.
To set up the operating mode:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Administration > Operation Mode tab.
- Select any of these operation modes:
- Wireless router mode / AiMesh Router mode (Default):
In wireless router mode, the wireless router connects to the Internet and provides Internet access to available devices on its own local network.
- Access Point(AP) / AiMesh Router in AP mode: In this mode, the router creates a new wireless network on an exising network.
- Repeater mode: In Repeater mode, GT-AXE11000 wirelessly connects to an existing wireless network to extend the wireless coverage. In this mode, the firewall, IP sharing, and NAT functions are disabled.
- Media Bridge: This setup requires two wireless routers. The second router serves as a media bridge where multiple devices such as Smart TVs and gaming consoles can be connected via ethernet.
- AiMesh node: This setup requires at least two ASUS routers which support AiMesh. Enable AiMesh node, and log in AiMesh router web UI to search for available AiMesh nodes nearby to join your AiMesh system. AiMesh system provides whole-home coverage and centralized management.
3. Click Apply.
NOTE: The router will reboot when you change the modes.
10.2 System
The System page allows you to configure your wireless router settings.
To set up the System settings:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Administration > System tab.
- You can configure the following settings:
- Change router login password: You can change the password and login name for the wireless router by entering a new name and password.
- Time Zone: Select the time zone for your network.
- NTP Server: The wireless router can access a NTP (Network time Protocol) server in order to synchronize the time.
- Enable Telnet: Click Yes to enable Telnet services on the network. Click No to disable Telnet.
- Authentication Method: You can select HTTP, HTTPS, or both protocols to secure router access.
- Enable Web Access from WAN: Select Yes to allow devices outside the network to access the wireless router GUI settings. Select No to prevent access.
- Allow only specified IP address: Click Yes if you want to specify the IP addresses of devices that are allowed access to the wireless router GUI settings from WAN.
- Client List: Enter the WAN IP addresses of networking devices allowed to access the wireless router settings. This list will be used if you clicked Yes in the Only allow specific IP item.
- Click Apply.
10.3 Firmware Upgrade
NOTE: Download the latest firmware from the ASUS website at http://www.asus.com
To upgrade the firmware:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Administration > Firmware Upgrade tab.
- In the New Firmware File field, click Browse to locate the downloaded file.
- Click Upload.
NOTES:
- When the upgrade process is complete, wait for some time for the system to reboot.
- If the upgrade process fails, the wireless router automatically enters rescue mode and the power LED indicator on the front panel starts flashing slowly. To recover or restore the system, refer to section 5.2 Firmware Restoration.
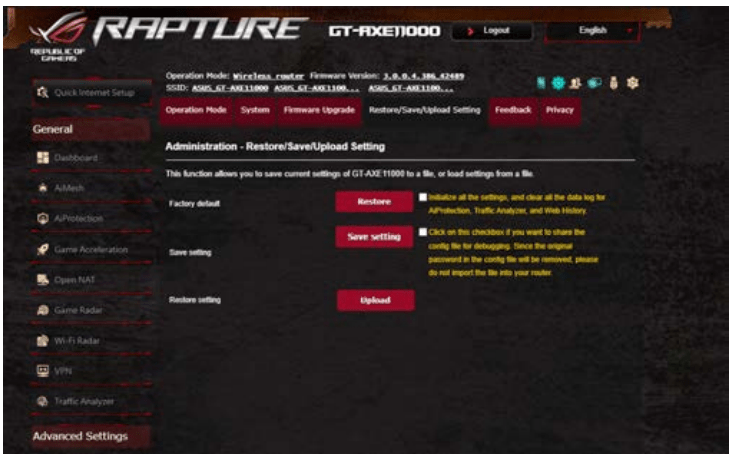
10.4 Restore/Save/Upload Setting
To restore/save/upload wireless router settings:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Administration > Restore/Save/Upload Setting tab.
- Select the tasks that you want to do:
- To restore to the default factory settings, click Restore, and click OK in the confirmation message.
- To save the current system settings, click Save, navigate to the folder where you intend to save the file and click Save.
- To restore from a saved system settings file, click Browse to locate your file, then click Upload.
IMPORTANT! If issues occur, upload the latest firmware version and configure new settings. Do not restore the router to its default settings.
11. System Log
System Log contains your recorded network activities.
NOTE: System log resets when the router is rebooted or powered off.
To view your system log:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > System Log.
- You can view your network activities in any of these tabs:
- General Log
- Wireless Log
- DHCP Leases
- IPv6
- Routing Table
- Port Forwarding
- Connections
12. Smart Connect
Smart Connect is designed to automatically steer clients to one of three radios (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz) to maximize total wireless throughput use.
12.1 Setting up Smart Connect
You can enable Smart Connect from the Web GUI through the following two ways:
• Via the Wireless screen
- On your web browser, manually key in the wireless router’s default IP address: http://router.asus.com.
- On the login page, key in the default user name (admin) and password (admin) and click OK. The QIS page launches automatically.
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > Wireless > General tab.
- Move the slider to ON in the Enable Smart Connect field. This function automatically connect the clients in your network to the appropriate band for optimal speed.
12.2 Smart Connect Rule
ASUSWRT provides default condition settings to trigger switching mechanism. You can also change the trigger conditions according to your networking surroundings. To change the settings, go to the Smart Connect Rule tab on the Network Tools screen.
Smart Connect Rule controls are divided into four sections:
- Steering Trigger Condition
- STA Selection Policy
- Interface Select and Qualify Procedures
- Bounce Detect
Steering Trigger Condition
This set of controls sets the criteria to initiate band steering.
- Bandwidth Utilization When bandwidth use exceeds this percentage, steering will be initiated.
- Enable Load Balance This controls load balancing.
- RSSI If the received signal level of any associated client meets this criteria, steering will be triggered.
- PHY Rate Less / PHY Rate Greater These controls determine STA link rates that trigger band steering.
- VHT This controls determines how 802.11ac and non-ac clients are handled.
- ALL (default) means any type of client can trigger steering.
- AC only means a client must support 802.11ac to trigger steering.
- Not-allowed means only non-802.11ac clients will trigger steering, i.e. 802.11a/b/g/n.
STA Selection Policy
Once steering has been triggered, ASUSWRT will follow the STA Selection Policy to select a client(STA) that is going to be steered to the most appropriate band.
Interface Select and Qualify Procedures
These controls determine where the steered client will end up. The Target Band controls specify first and second choice of steering targets. Clients meeting the STA selection policy criteria for the radio will be steered to the first target if that radio’s Bandwidth Utilization is less than the set value. Otherwise, the client will be sent to the second Target Band radio.
Bounce Detect
This set of controls determines how often a client can be steered.
This is intended to prevent clients from constantly moving around. It does not, however, prevent clients from disconnecting on their own, or counting them as bounces if they do. Each client can be steered N Counts within the Window Time. When the Count limit is hit, the client will not be steered again for Dwell Time.
UTILITIES
NOTES:
- Download and install the wireless router's utilities from the ASUS website:
- Device Discovery v1.4.7.1 at http://dlcdnet.asus.com/pub/ASUS/ LiveUpdate/Release/Wireless/Discovery.zip
- Firmware Restoration v1.9.0.4 at http://dlcdnet.asus.com/pub/ ASUS/LiveUpdate/Release/Wireless/Rescue.zip
- Windows Printer Utility v1.0.5.5 at http://dlcdnet.asus.com/pub/ ASUS/LiveUpdate/Release/Wireless/Printer.zip
- The utilities are not supported on MAC OS.
1. Device Discovery
Device Discovery is an ASUS WLAN utility that detects an ASUS wireless router device, and allows you to configure the wireless networking settings.
To launch the Device Discovery utility:
• From your computer’s desktop, click Start > All Programs > ASUS Utility > ASUS Wireless Router > Device Discovery.
NOTE: When you set the router to Access Point mode, you need to use Device Discovery to get the router’s IP address.
2. Firmware Restoration
Firmware Restoration is used on an ASUS Wireless Router that failed during its firmware upgrading process. It uploads the firmware that you specify. The process takes about three to four minutes.
IMPORTANT! Launch the rescue mode on the router before using the Firmware Restoration utility.
NOTE: This feature is not supported on MAC OS.
To launch the rescue mode and use the Firmware Restoration utility:
1. Unplug the wireless router from the power source.
2. Hold the Reset button at the rear panel and simultaneously replug the wireless router into the power source. Release the Reset button when the Power LED at the front panel flashes slowly, which indicates that the wireless router is in the rescue mode.
3. Set a static IP on your computer and use the following to set up your TCP/IP settings:
IP address: 192.168.1.x
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
4. From your computer’s desktop, click Start > All Programs > ASUS Utility GT-AXE11000 Wireless Router > Firmware Restoration.
5. Specify a firmware file, then click Upload.
NOTE: This is not a firmware upgrade utility and cannot be used on a working ASUS Wireless Router. Normal firmware upgrades must be done through the web interface. Refer to Chapter 4: Configuring the Advanced Settings for more details.
3. Setting up your printer server
3.1 ASUS EZ Printer Sharing
ASUS EZ Printing Sharing utility allows you to connect a USB printer to your wireless router’s USB port and set up the print server. This allows your network clients to print and scan files wirelessly.
NOTE: The print server function is supported on Windows® 7/8/8.1/10.
To set up the EZ Printer sharing mode:
- From the navigation panel, go to Advanced Settings > USB Application > Network Printer Server.
- Click Download Now! to download the network printer utility.
NOTE: Network printer utility is supported on Windows® 7/8/8.1/10. To install the utility on Mac OS, select Use LPR protocol for sharing printer.
3. Unzip the downloaded file and click the Printer icon to run the network printer setup program.
4. Follow the onscreen instructions to set up your hardware, then click Next.
5. Wait a few minutes for the initial setup to finish. Click Next.
6. Click Finish to complete the installation.
7. Follow the Windows® OS instructions to install the printer driver.
8. After the printer’s driver installation is complete, network clients can now use the printer.
3.2 Using LPR to Share Printer
You can share your printer with computers running on Windows® and MAC operating system using LPR/LPD (Line Printer Remote/ Line Printer Daemon).
Sharing your LPR printer To share your LPR printer:
1. From the Windows® desktop, click Start > Devices and Printers > Add a printer to run the Add Printer Wizard.
2. Select Add a local printer and then click Next.
3. Select Create a new port then set Type of Port to Standard TCP/IP Port. Click Next.
4. In the Hostname or IP address field, key in the IP address of the wireless router then click Next.
5. Select Custom then click Settings.
6. Set Protocol to LPR. In the Queue Name field, key in LPRServer then click OK to continue.
7. Click Next to finish setting up the standard TCP/IP port.
8. Install the printer driver from the vendor-model list. If your printer is not in the list, click Have Disk to manually install the printer drivers from a CD-ROM or file.
9. Click Next to accept the default name for the printer.
10. Click Finish to complete the installation.
4. Download Master
Download Master is a utility that helps you download files even while your laptops or other devices are switched off.
NOTE: You need a USB device connected to the wireless router to use Download Master.
To use Download Master:
1. Click Advanced Settings > USB Application > Download Master to download and install the utility automatically.
NOTE: If you have more than one USB drive, select the USB device you want to download the files to.
2. After the download process is finished, click the Download Master icon to start using the utility.
3. Click Add to add a download task.
4. Select a download type such as BitTorrent, HTTP, or FTP. Provide a torrent file or a URL to begin downloading.
NOTE: For details on Bit Torrent, refer to section 5.4.1 Configuring the Bit Torrent download settings.
5. Use the navigation panel to configure the advanced settings.
4.1 Configuring Bit Torrent download settings
To configure BitTorrent download settings:
- From Download Master’s navigation panel, click Bit Torrent to launch the Bit Torrent Setting page.
- Select a specific port for your download task.
- To prevent network congestion, you can limit the maximum upload and download speeds under Speed Limits.
- You can limit the maximum number of allowed peers and enable or disable file encryption during downloads.
4.2 NZB settings
You can set up a USENET server to download NZB files. After entering USENET settings, Apply.
TROUBLESHOOTING
This chapter provides solutions for issues you may encounter with your router. If you encounter problems that are not mentioned in this chapter, visit the ASUS support site at: https://www.asus.com/support for more product information and contact details of ASUS Technical Support.
Basic Troubleshooting
If you are having problems with your router, try these basic steps in this section before looking for further solutions.
Upgrade Firmware to the latest version.
- Launch the Web GUI. Go to Advanced Settings > Administration > Firmware Upgrade tab. Click Check to verify if the latest firmware is available.
- If the latest firmware is available, visit the ASUS global website at https://rog.asus.com/networking/rog-rapture-gt-axe11000model/helpdesk_download to download the latest firmware.
- From the Firmware Upgrade page, click Browse to locate the firmware file.
- Click Upload to upgrade the firmware.
Restart your network in the following sequence:
- Turn off the modem.
- Unplug the modem.
- Turn off the router and computers.
- Plug in the modem.
- Turn on the modem and then wait for 2 minutes.
- Turn on the router and then wait for 2 minutes.
- Turn on computers.
Check if your Ethernet cables are plugged properly.
- When the Ethernet cable connecting the router with the modem is plugged in properly, the WAN LED will be on.
- When the Ethernet cable connecting your poweredon computer with the router is plugged in properly, the corresponding LAN LED will be on.
Check if the wireless setting on your computer matches that of your computer.
- When you connect your computer to the router wirelessly, ensure that the SSID (wireless network name), encryption mehtod, and password are correct.
Check if your network settings are correct.
- Each client on the network should have a valid IP address. ASUS recommends that you use the wireless router’s DHCP server to assign IP addresses to computers on your network.
- Some cable modem service providers require you to use the MAC address of the computer initially registered on the account. You can view the MAC address in the web GUI, Network Map > Clients page, and hover the mouse pointer over your device in Client Status.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
I cannot access the router GUI using a web browser
- If your computer is wired, check the Ethernet cable connection and LED status as described in the previous section.
- Ensure that you are using the correct login information. The default factory login name and password is “admin/admin”. Ensure that the Caps Lock key is disabled when you enter the login information.
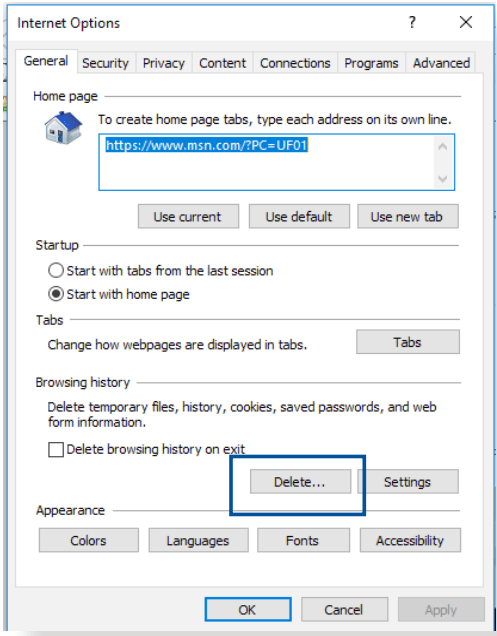
- Delete the cookies and files in your web browser. For Internet Explorer, follow these steps:
Launch Internet Explorer, then click Tools > Internet Options.
In the General tab, under Browsing history, click Delete…, select Temporary Internet files and website files and Cookies and website data then click Delete.
NOTES:
- The commands for deleting cookies and files vary with web browsers.
- Disable proxy server settings, cancel the dial-up connection, and set the TCP/IP settings to obtain IP addresses automatically. For more details, refer to Chapter 1 of this user manual.
- Ensure that you use CAT5e or CAT6 ethernet cables.
The client cannot establish a wireless connection with the router.
NOTE: If you are having issues connecting to 5GHz network, make sure that your wireless device supports 5GHz or features dual band capabilities.
- Out of Range:
- Move the router closer to the wireless client.
- Try to adjust antennas of the router to the best direction as described in section 1.4 Positioning your router.
- DHCP server has been disabled:
- Launch the web GUI. Go to Advanced Settings > Network Map> Clients and search for the device that you want to connect to the router.
- If you cannot find the device in the Network Map, go to Advanced Settings > LAN > DHCP Server, Basic Config list, select Yes on the Enable the DHCP Server.
- SSID has been hidden. If your device can find SSIDs from other routers but cannot find your router’s SSID, go to Advanced Settings > Wireless > General, select No on Hide SSID, and select Auto on Control Channel.
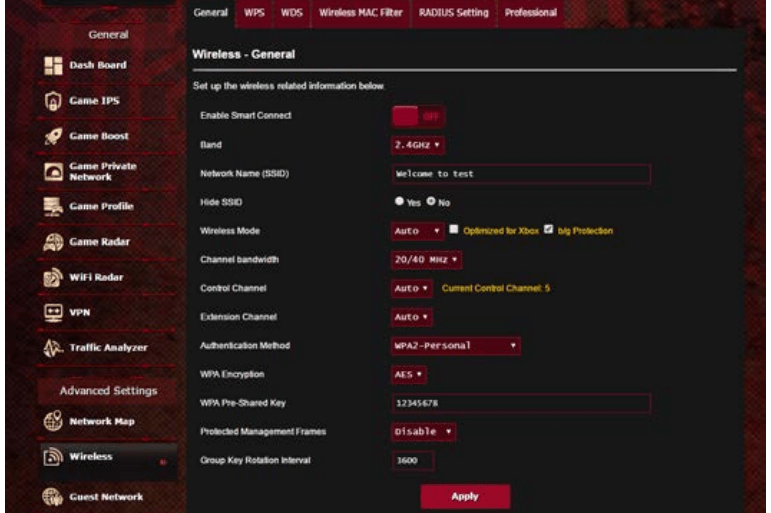
- If you are using a wireless LAN adapter, check if the wireless channel in use conforms to the channels available in your country/area. If not, adjust the channel, channel bandwidth, and wireless mode.
- If you still cannot connect to the router wirelessly, you can reset your router to factory default settings. In the router GUI,click Administration > Restore/Save/Upload Setting and click Restore.
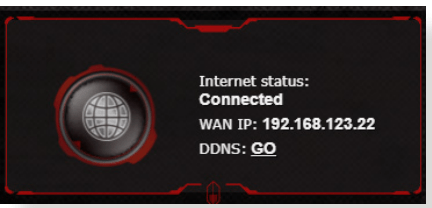
Internet is not accessible.
- Check if your router can connect to your ISP’s WAN IP address. To do this, launch the web GUI and go to Advanced Settings> Network Map, and check the Internet Status.
- If your router cannot connect to your ISP’s WAN IP address, try restarting your network as described in the section Restart your network in following sequence under Basic Troubleshooting.
- The device has been blocked via the Parental Control function. Go to General > AiProtection > Parental Controls tab and see if the device is in the list. If the device is listed under Client Name, remove the device using the Delete button or adjust the Time Management Settings.
- If there is still no Internet access, try to reboot your computer and verify the network’s IP address and gateway address.
- Check the status indicators on the ADSL modem and the wireless router. If the WAN LED on the wireless router is not ON, check if all cables are plugged properly.
You forgot the SSID (network name) or network password
- Setup a new SSID and encryption key via a wired connection (Ethernet cable). Launch the web GUI, go to Network Map, click the router icon, enter a new SSID and encryption key, and then click Apply.
- Reset your router to the default settings. Launch the web GUI, go to Administration > Restore/Save/Upload Setting, and click Restore. The default login account and password are both “admin”.
How to restore the system to its default settings?
- Go to Administration > Restore/Save/Upload Setting, and click Restore.
The following are the factory default settings:
User Name: | admin |
Password: | admin |
Enable DHCP: | Yes (if WAN cable is plugged in) |
IP address: | http://router.asus.com (or 192.168.1.1) |
Domain Name: | (Blank) |
Subnet Mask: | 255.255.255.0 |
DNS Server 1: | 192.168.1.1 |
DNS Server 2: | (Blank) |
SSID (2.4GHz): | ASUS_XX_2G |
SSID (5GHz): | ASUS_XX_5G |
SSID (6GHz): | ASUS_XX_6G |
Firmware upgrade failed.
Launch the rescue mode and run the Firmware Restoration utility. Refer to section 5.2 Firmware Restoration on how to use the Firmware Restoration utility.
Cannot access Web GUI
Before configuring your wireless router, do the steps described in this section for your host computer and network clients.
A. Disable the proxy server, if enabled.
Windows®
- Click Start > Internet Explorer to launch the browser.
- Click Tools > Internet options > Connections tab > LAN settings.
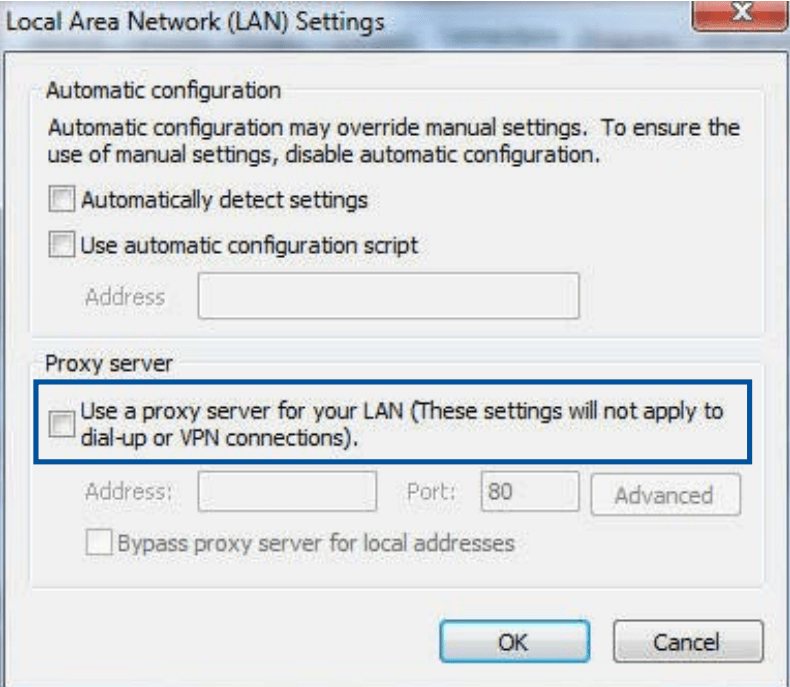
- From the Local Area Network (LAN) Settings screen, untick Use a proxy server for your LAN.
- Click OK when done.

MAC OS
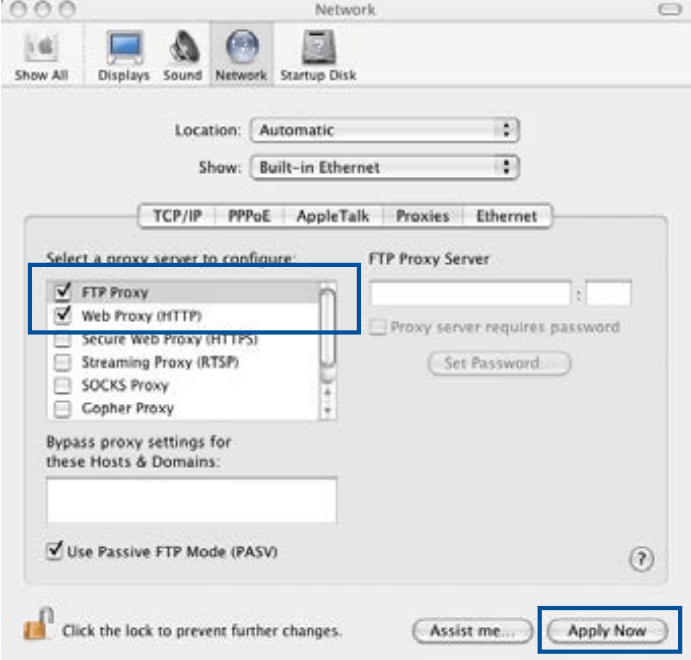
- From your Safari browser, click Safari > Preferences > Advanced > Change Settings...
- From the Network screen, deselect FTP Proxy and Web Proxy (HTTP).
- Click Apply Now when done.
NOTE: Refer to your browser's help feature for details on disabling the proxy server.
B. Set the TCP/IP settings to automatically obtain an IP address.
Windows®
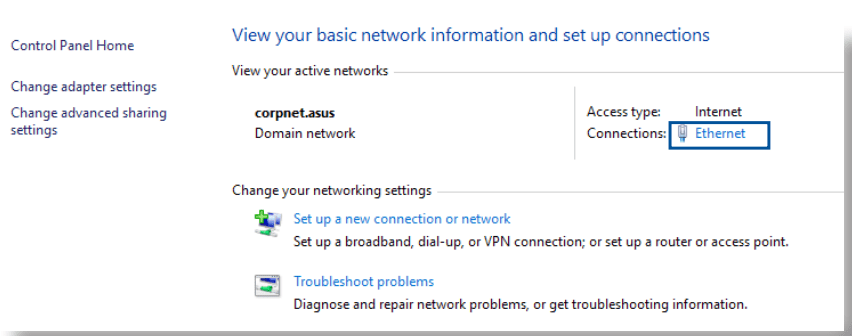
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center, then click the network connection to display its status window.
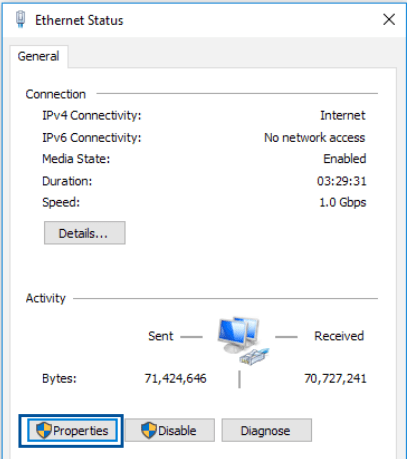
2. Click Properties to display the Ethernet Properties window.
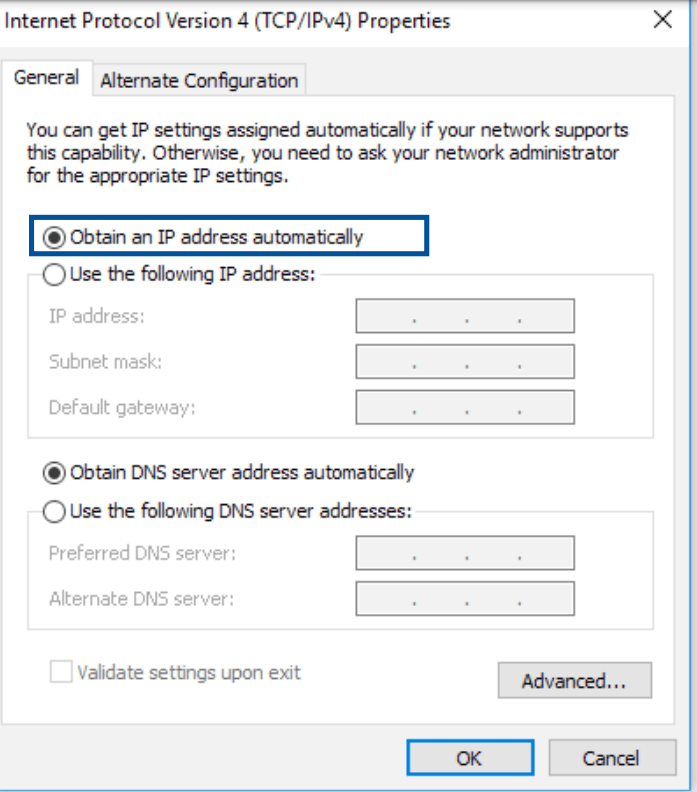
3. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) or Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6), then click Properties.
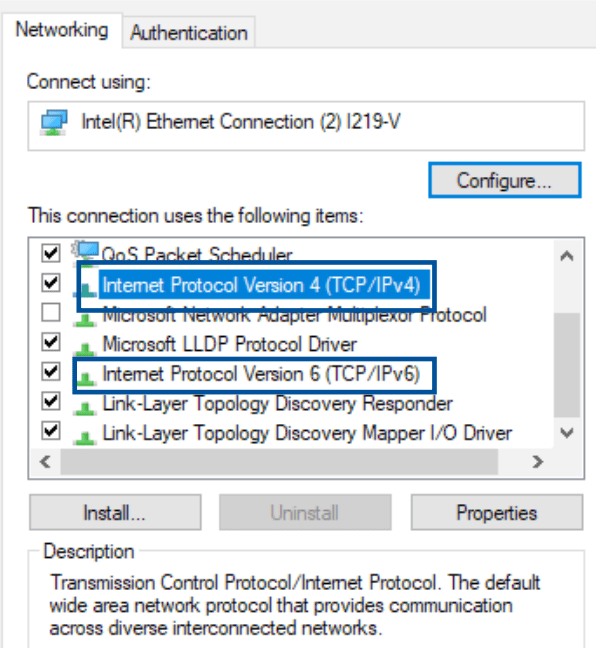
4. To obtain the IPv4 IP settings automatically, tick Obtain an IP address automatically.
To obtain the IPv6 IP settings automatically, tick Obtain an IPv6 address automatically.
5. Click OK when done.
NOTE: Refer to your operating system’s help and support feature for details on configuring your computer’s TCP/IP settings.
C. Disable the dial-up connection, if enabled.
Windows®
- Click Start > Internet Explorer to launch the browser.
- Click Tool > Internet Explorer > Connections tab.
- Tick Never dial a connection.
- Click OK when done.
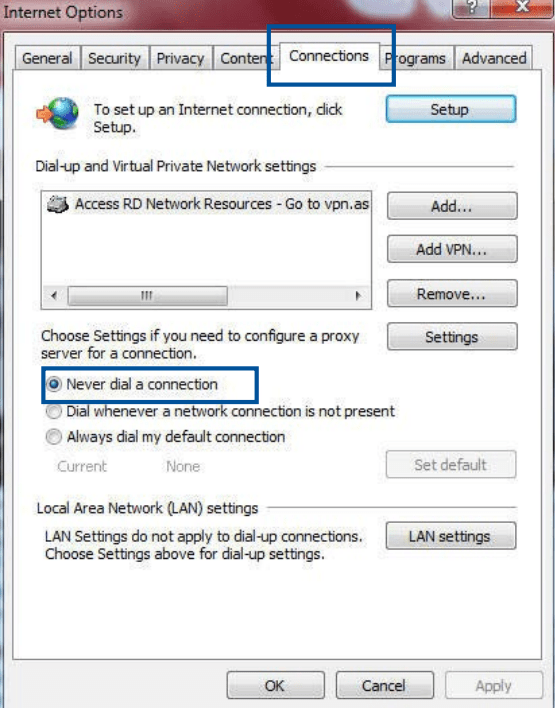
NOTE: Refer to your browser's help feature for details on disabling the dial-up connection.
See other models: GT-AXE11000 RT-AX89X GT-AX11000 RT-AC86U L210MA-DB01
