Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...
88
5.4.2.2.2. ONVIF
The ONVIF tab is where users can configure authentication via the ONVIF standard. Below is a screenshot of the ONVIF settings
tab:
To enable ONVIF, click the radio button next to Enable, and then click the save button.
To reset to default settings, click the Reset Defaults button. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button. To save the settings,
click the Save button.
5.4.2.3. DDNS
DDNS stands for Dynamic Domain Name Server. This technology is used to automatically update name servers in real time to help
the camera maintain a persistent address despite changes in location or configuration. What this means is that even when the
camera is restarted, moved, or reconfigured, it can keep the same IP address, thus allowing remote users uninterrupted access to
the camera, rather than having to request a new IP address to use for remote access anytime a change is made.
To use this feature, users will need to setup an account with a DDNS service. The camera supports a variety of DDNS services such
as Quick DDNS, NO-IP DDNS, CN99 DDNS, and Dyndns DDNS. Based on which service is selected, different options may show on
this screen. For purposes of this guide, AmcrestDDNS will be used. AmcrestDDNS is a free DDNS service provided by Amcrest, and
it must be renewed every year. A renewal reminder email will be sent to the email entered in the username field below.
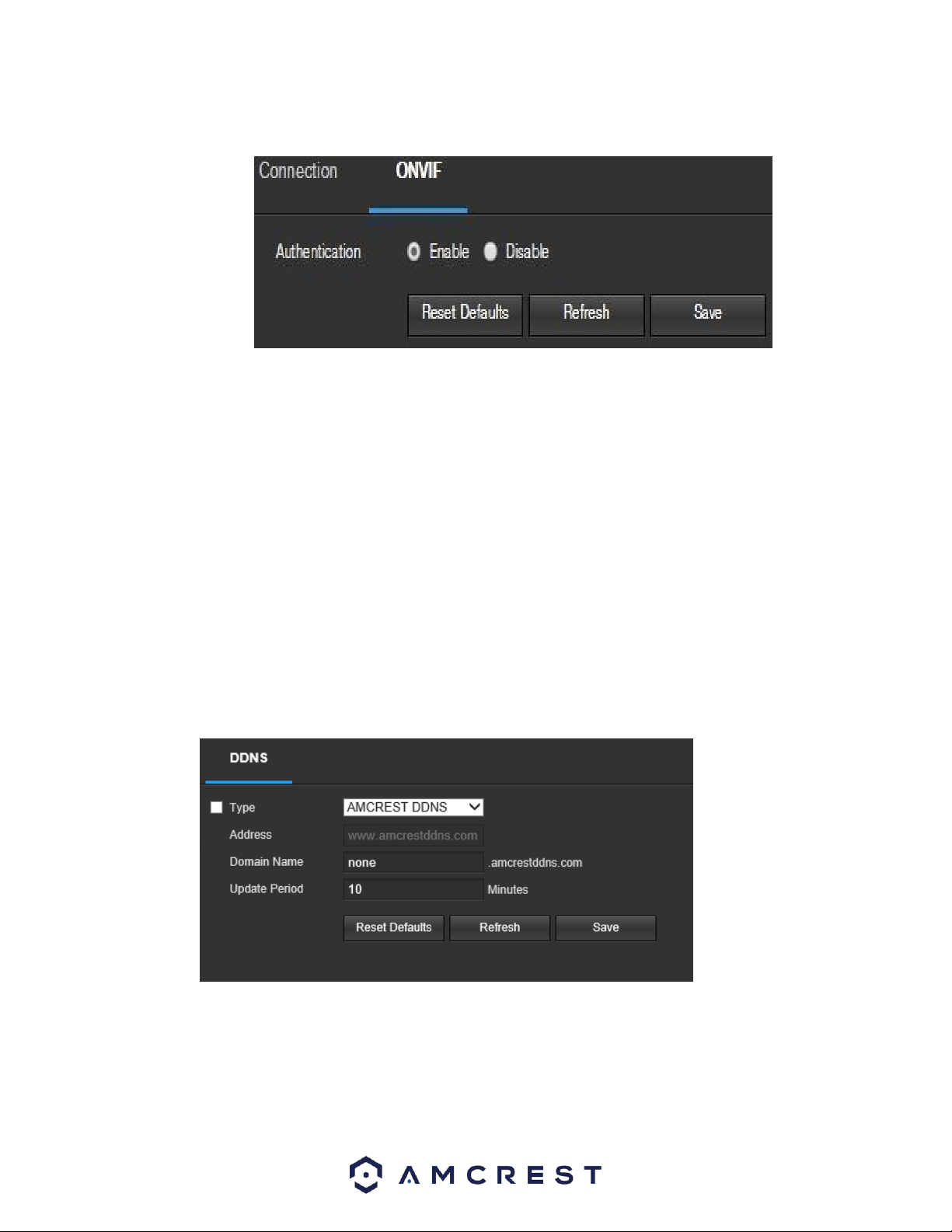
Below is a screenshot of the DDNS settings screen, configured to AmcrestDDNS:
To reset to default settings, click the Reset Defaults button. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button.
To save the settings, click the Save button.
Loading ...
Loading ...
Loading ...